Gegeben a spezieller Binärbaum wessen Blattknoten sind zu a verbunden kreisförmige doppelt verknüpfte Liste Die Aufgabe besteht darin, das zu finden Höhe des Baumes.
Beispiele:
Eingang:

Ausgabe: 2
Erläuterung: Die Höhe des Binärbaums nach der Erkennung der Blattknoten beträgt 2. Im obigen Binärbaum sind 6, 5 und 4 Blattknoten und bilden eine kreisförmige doppelt verknüpfte Liste. Hier fungiert der linke Zeiger des Blattknotens als vorheriger Zeiger der kreisförmigen doppelt verknüpften Liste und sein rechter Zeiger als nächster Zeiger der kreisförmigen doppelt verknüpften Liste.Eingang:
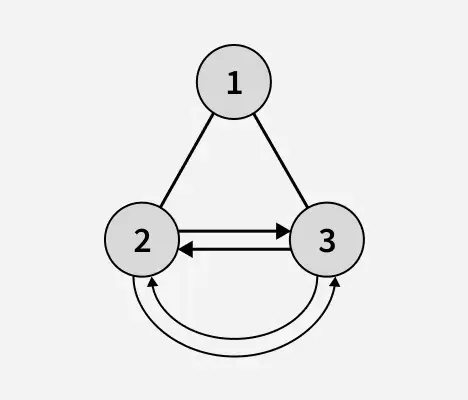
Ausgabe: 1
Erläuterung: Die Höhe des Binärbaums nach der Erkennung der Blattknoten beträgt 1. Im obigen Binärbaum sind 2 und 3 Blattknoten und bilden eine kreisförmige, doppelt verknüpfte Liste.
Ansatz :
C++Die Idee ist, zu folgen ähnlicher Ansatz wie wir es tun Ermitteln der Höhe eines normalen Binärbaums . Wir rekursiv berechnen Höhe von links und rechts Teilbäume eines Knotens und zuweisen Höhe zum Knoten als max der Körpergrößen von zwei Kindern plus 1. Aber linkes und rechtes Kind von a Blattknoten sind für normale Binärbäume null. Aber hier ist der Blattknoten ein kreisförmiger doppelt verknüpfter Listenknoten. Damit ein Knoten ein Blattknoten ist, prüfen wir, ob Knoten ist links und rechts zeigt auf die Knoten und es ist rechts ist links weist auch darauf hin Knoten selbst.
// C++ program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list #include
// C program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list #include
// Java program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node static boolean isLeaf(Node node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left != null && node.left.right == node && node.right != null && node.right.left == node; } // Compute the height of a tree static int findTreeHeight(Node node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node == null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node l1 = root.left.left.left; Node l2 = root.left.right; Node l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; System.out.println(findTreeHeight(root)); } }
# Python program to calculate height of a special tree # whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None # function to check if given # node is a leaf node or node def isLeaf(node): # For a node to be a leaf node it should # satisfy the following two conditions: # 1. Node's left's right pointer should be # current node. # 2. Node's right's left pointer should be # current node. # If one condition is met it is guaranteed # that the other condition is also true. return (node.left and node.left.right == node and node.right and node.right.left == node) # Compute the height of a tree def findTreeHeight(node): # if node is NULL return -1. if node is None: return -1 # if node is a leaf node return 0 if isLeaf(node): return 0 # compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)) if __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) root.left.left.left = Node(6) # Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes l1 = root.left.left.left l2 = root.left.right l3 = root.right # create circular doubly linked list out of # leaf nodes of the tree # set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2 l2.right = l3 l3.right = l1 # set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2 l2.left = l1 l1.left = l3 print(findTreeHeight(root))
// C# program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node static bool isLeaf(Node node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left != null && node.left.right == node && node.right != null && node.right.left == node; } // Compute the height of a tree static int findTreeHeight(Node node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node == null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.Max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } static void Main(string[] args) { Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node l1 = root.left.left.left; Node l2 = root.left.right; Node l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; Console.WriteLine(findTreeHeight(root)); } }
// JavaScript program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node function isLeaf(node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left && node.left.right === node && node.right && node.right.left === node; } // Compute the height of a tree function findTreeHeight(node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node === null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes const l1 = root.left.left.left; const l2 = root.left.right; const l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; console.log(findTreeHeight(root));
Ausgabe
3
Zeitkomplexität: O(n) wo N ist die Anzahl der Knoten.
Nebenraum: Oh)


