Gegeben a Binärbaum Die Aufgabe besteht darin umdrehen der Binärbaum in Richtung richtige Richtung n das ist im Uhrzeigersinn.
Eingang:
Java-Array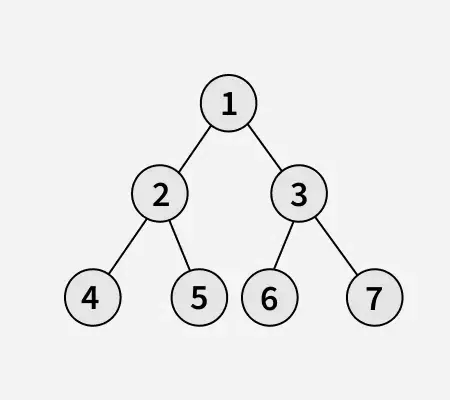
Ausgabe:
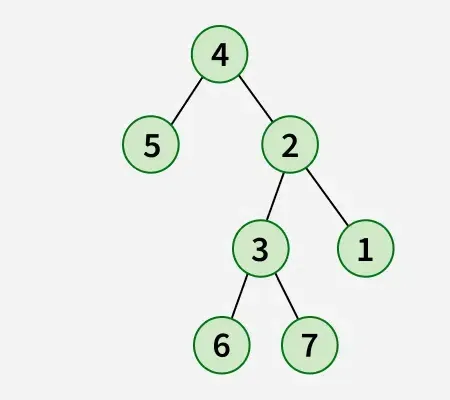
Erläuterung: Bei der Flip-Operation wird der am weitesten links stehende Knoten zur Wurzel des umgedrehten Baums und sein übergeordneter Knoten wird zu seinem rechten untergeordneten Element und der rechte Geschwisterknoten wird zu seinem linken untergeordneten Element. Dasselbe sollte für alle am weitesten links stehenden Knoten rekursiv durchgeführt werden.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
ReactJS-Karte
- [Erwarteter Ansatz – 1] Rekursion verwenden – O(n) Zeit und O(n) Raum
- [Erwarteter Ansatz – 2] Iterativer Ansatz – O(n) Zeit und O(1) Raum
[Erwarteter Ansatz – 1] Rekursion verwenden – O(n) Zeit und O(n) Raum
Die Idee ist rekursiv Drehen Sie den Binärbaum um, indem Sie die vertauschen links Und Rechts Teilbäume jedes Knotens. Nach dem Umdrehen wird die Struktur des Baums umgekehrt und die neue Wurzel des umgedrehter Baum wird der ursprüngliche Blattknoten ganz links sein.
Unten ist das Wichtigste Rotationscode eines Teilbaums:
- root->left->left = root->right
- root->left->right = root
- root->left = NULL
- root->right = NULL
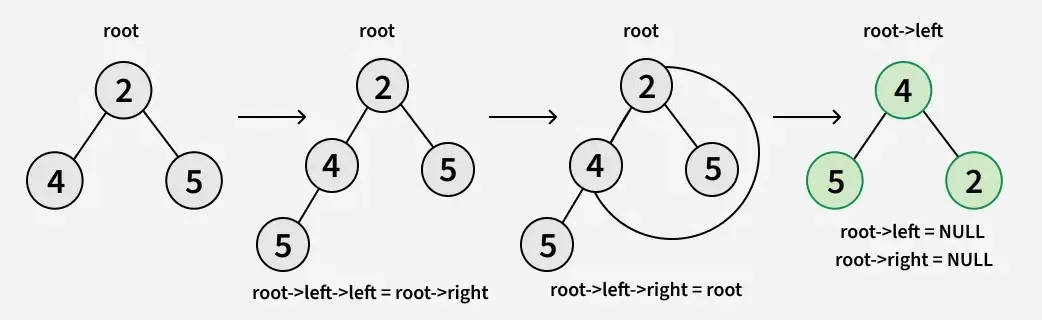
Nachfolgend finden Sie die Umsetzung des oben genannten Ansatzes:
C++// C++ program to flip a binary tree // using recursion #include
// Java program to flip a binary tree // using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root) { // Base cases if (root == null) return root; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root; // Recursively call the same method Node flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root.left.left = root.right; root.left.right = root; root.left = root.right = null; return flippedRoot; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void printLevelOrder(Node root) { // Base Case if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal java.util.Queue<Node> q = new java.util.LinkedList<>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.add(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.size(); // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.poll(); System.out.print(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.add(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.add(node.right); nodeCount--; } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(root); } }
# Python program to flip a binary # tree using recursion class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None def flipBinaryTree(root): # Base cases if root is None: return root if root.left is None and root.right is None: return root # Recursively call the same method flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left) # Rearranging main root Node after returning # from recursive call root.left.left = root.right root.left.right = root root.left = root.right = None return flippedRoot # Iterative method to do level order # traversal line by line def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue for # level order traversal queue = [] queue.append(root) while queue: nodeCount = len(queue) while nodeCount > 0: node = queue.pop(0) print(node.data end=' ') if node.left is not None: queue.append(node.left) if node.right is not None: queue.append(node.right) nodeCount -= 1 print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Make a binary tree # # 1 # / # 2 3 # / # 4 5 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.right.left = Node(4) root.right.right = Node(5) root = flipBinaryTree(root) printLevelOrder(root)
// C# program to flip a binary tree // using recursion using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node FlipBinaryTree(Node root) { if (root == null) return root; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root; // Recursively call the same method Node flippedRoot = FlipBinaryTree(root.left); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root.left.left = root.right; root.left.right = root; root.left = root.right = null; return flippedRoot; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void PrintLevelOrder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.Enqueue(root); while (q.Count > 0) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.Count; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.Dequeue(); Console.Write(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.Enqueue(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.Enqueue(node.right); nodeCount--; } Console.WriteLine(); } } static void Main(string[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = FlipBinaryTree(root); PrintLevelOrder(root); } }
// JavaScript program to flip a binary // tree using recursion class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Method to flip the binary tree function flipBinaryTree(root) { if (root === null) return root; if (root.left === null && root.right === null) return root; // Recursively call the same method const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root.left.left = root.right; root.left.right = root; root.left = root.right = null; return flippedRoot; } // Iterative method to do level order traversal // line by line function printLevelOrder(root) { if (root === null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal const queue = [root]; while (queue.length > 0) { let nodeCount = queue.length; while (nodeCount > 0) { const node = queue.shift(); console.log(node.data + ' '); if (node.left !== null) queue.push(node.left); if (node.right !== null) queue.push(node.right); nodeCount--; } console.log(); } } // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(flippedRoot);
Ausgabe
2 3 1 4 5
[Erwarteter Ansatz – 2] Iterativer Ansatz - O(n) Zeit und O(n) Raum
Der iterative Lösung folgt dem gleichen Ansatz wie die rekursiv Das Einzige, worauf wir achten müssen, ist sparen die Knoteninformationen, die sein werden überschrieben .
Nachfolgend finden Sie die Umsetzung des oben genannten Ansatzes:
C++// C++ program to flip a binary tree using // iterative approach #include
// Java program to flip a binary tree // using iterative approach class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root) { // Initializing the pointers to do the // swapping and storing states Node curr = root; Node next = null; Node prev = null; Node ptr = null; while (curr != null) { // Pointing the next pointer to // the current next of left next = curr.left; // Making the right child of // prev as curr left child curr.left = ptr; // Storing the right child // of curr in ptr ptr = curr.right; curr.right = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void printLevelOrder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal java.util.Queue<Node> q = new java.util.LinkedList<>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize // height q.add(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.size(); // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.poll(); System.out.print(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.add(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.add(node.right); nodeCount--; } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(root); } }
# Python program to flip a binary tree # using iterative approach class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Method to flip the binary tree # iteratively def flip_binary_tree(root): # Initializing the pointers to do # the swapping and storing states curr = root next = None prev = None ptr = None while curr is not None: # Pointing the next pointer to the # current next of left next = curr.left # Making the right child of prev # as curr left child curr.left = ptr # Storing the right child of # curr in ptr ptr = curr.right curr.right = prev prev = curr curr = next return prev # Iterative method to do level order # traversal line by line def printLevelOrder(root): if root is None: return # Create an empty queue for # level order traversal queue = [] queue.append(root) while queue: nodeCount = len(queue) while nodeCount > 0: node = queue.pop(0) print(node.data end=' ') if node.left is not None: queue.append(node.left) if node.right is not None: queue.append(node.right) nodeCount -= 1 print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Make a binary tree # # 1 # / # 2 3 # / # 4 5 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.right.left = Node(4) root.right.right = Node(5) root = flip_binary_tree(root) printLevelOrder(root)
// C# program to flip a binary tree // using iterative approach using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node FlipBinaryTree(Node root) { // Initializing the pointers to // do the swapping and storing states Node curr = root; Node next = null; Node prev = null; Node ptr = null; while (curr != null) { // Pointing the next pointer to // the current next of left next = curr.left; // Making the right child of prev // as curr left child curr.left = ptr; // Storing the right child // of curr in ptr ptr = curr.right; curr.right = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void PrintLevelOrder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for // level order traversal Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.Enqueue(root); while (q.Count > 0) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.Count; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.Dequeue(); Console.Write(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.Enqueue(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.Enqueue(node.right); nodeCount--; } Console.WriteLine(); } } static void Main(string[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = FlipBinaryTree(root); PrintLevelOrder(root); } }
// JavaScript program to flip a binary // tree using iterative approach class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function flipBinaryTree(root) { // Initializing the pointers to do the // swapping and storing states let curr = root; let next = null; let prev = null; let ptr = null; while (curr !== null) { // Pointing the next pointer to the // current next of left next = curr.left; // Making the right child of prev // as curr left child curr.left = ptr; // Storing the right child of // curr in ptr ptr = curr.right; curr.right = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line function printLevelOrder(root) { if (root === null) return; // Create an empty queue for // level order traversal const queue = [root]; while (queue.length > 0) { let nodeCount = queue.length; while (nodeCount > 0) { const node = queue.shift(); console.log(node.data + ' '); if (node.left !== null) queue.push(node.left); if (node.right !== null) queue.push(node.right); nodeCount--; } console.log(); } } // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(flippedRoot);
Ausgabe
2 3 1 4 5



