Gegeben eine Reihe von N Elemente und zwei ganze Zahlen ein b die zum angegebenen Array gehören. Erstellen Sie eine Binärer Suchbaum durch Einfügen von Elementen aus arr[0] bis arr[n-1] . Die Aufgabe besteht darin, das zu finden maximal Element im Pfad von a nach b.
Beispiel:
Eingabe: arr[] = { 18 36 9 6 12 10 1 8 } a = 1 b = 10.
Ausgabe : 12
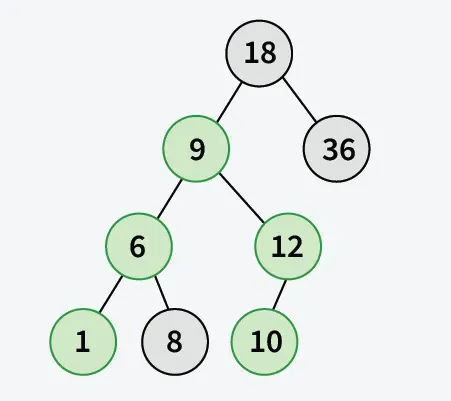
Erläuterung: Weg von 1 bis 10 enthält { 1 6 9 12 10 } . Das maximale Element ist 12.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- [Naiver Ansatz] Hashing verwenden – O(n * log n) Zeit und O(n) Raum
- [Erwarteter Ansatz] Verwendung der LCA von zwei Knoten – O(h)-Zeit und O(h)-Raum
[Naiver Ansatz] Hashing verwenden – O(n * log n) Zeit und O(n) Raum
Die Idee ist, a zu verwenden Hashmap um die zu speichern Elternteil Knoten jedes Knotens in der binärer Suchbaum . Wir können von beiden gegebenen Knoten ausgehen und den Baum nach oben durchlaufen und die in a angetroffenen Knoten speichern Satz . Sobald wir die Wurzel oder einen gemeinsamen Vorfahren der beiden Knoten erreicht haben, können wir den Baum von jedem Knoten aus durchqueren und den Knoten finden maximal Element, das in der Menge der Knoten angetroffen wird.
Java wandelt int in einen String um
Algorithmusschritte für den obigen Ansatz:
- Erstellen Sie ein Leerzeichen Hash-Tabelle um die zu speichern Elternteil Knoten jedes Knotens im binären Suchbaum.
- Führen Sie a aus Tiefensuche (DFS) Durchlaufen Sie den binären Suchbaum und füllen Sie die Hash-Tabelle mit dem übergeordneten Knoten jedes Knotens.
- Initialisieren Sie beispielsweise zwei Zeiger p1 und p2 zu den angegebenen Knoten.
- Initialisieren Sie beispielsweise zwei leere Mengen s1 und s2 um die beim Durchqueren des Baums angetroffenen Knoten zu speichern p1 und p2 jeweils.
- Während p1 und p2 Sind ungleich Gehen Sie wie folgt vor:
- Wenn p1 nicht null füge es zu Set s1 und hinzu aktualisieren p1 mithilfe der Hash-Tabelle an seinen übergeordneten Knoten.
- Wenn p2 nicht null füge es zu Set s2 hinzu und aktualisieren p2 mithilfe der Hash-Tabelle an seinen übergeordneten Knoten.
- Finden Sie die Schnittmenge von s1 und s2 d. h. die Menge der Knoten, die sowohl s1 als auch s2 gemeinsam sind.
- In dieser Kreuzung finden maximal Element und geben Sie es zurück.
Nachfolgend finden Sie die Umsetzung des oben genannten Ansatzes:
C++// C++ program to find maximum element in the path // between two Nodes of Binary Search Tree. #include
// Java program to find the maximum element in the path // between two Nodes of Binary Search Tree. import java.util.*; class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Insert a new Node in Binary Search Tree static void insertNode(Node root int x) { Node current = root parent = null; // Traverse to the correct position // for insertion while (current != null) { parent = current; if (x < current.data) current = current.left; else current = current.right; } // Insert new Node at the correct position if (parent == null) root = new Node(x); else if (x < parent.data) parent.left = new Node(x); else parent.right = new Node(x); } // DFS to populate parent map for each node static void dfs(Node root Map<Node Node> parentMap Node parent) { if (root == null) return; // Store the parent of the current node if (parent != null) { parentMap.put(root parent); } // Recur for left and right children dfs(root.left parentMap root); dfs(root.right parentMap root); } // Function to find the node with the given // value in the BST static Node findNode(Node root int val) { if (root == null) return null; if (root.data == val) return root; Node leftResult = findNode(root.left val); if (leftResult != null) return leftResult; return findNode(root.right val); } // Find maximum element in the path between // two nodes in BST static int findMaxElement(Node root int x int y) { Map<Node Node> parentMap = new HashMap<>(); // Populate parent map with DFS dfs(root parentMap null); // Find the nodes corresponding to // the values x and y Node p1 = findNode(root x); Node p2 = findNode(root y); // If nodes not found if (p1 == null || p2 == null) return -1; // Sets to store nodes encountered // while traversing up the tree Set<Node> s1 = new HashSet<>(); Set<Node> s2 = new HashSet<>(); // Variable to store the maximum element // in the path int maxElement = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // Traverse up the tree from p1 and p2 // and add nodes to sets s1 and s2 while (p1 != p2) { if (p1 != null) { s1.add(p1); maxElement = Math.max(maxElement p1.data); // Move to parent node p1 = parentMap.get(p1); } if (p2 != null) { s2.add(p2); maxElement = Math.max(maxElement p2.data); p2 = parentMap.get(p2); } // Check if there's a common node in both sets if (s1.contains(p2)) break; if (s2.contains(p1)) break; } // Now both p1 and p2 point to their // Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA) maxElement = Math.max(maxElement p1.data); return maxElement; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {18 36 9 6 12 10 1 8}; int a = 1 b = 10; int n = arr.length; Node root = new Node(arr[0]); for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) insertNode(root arr[i]); System.out.println(findMaxElement(root a b)); } }
# Python program to find maximum element in the path # between two Nodes of Binary Search Tree. class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Insert a new Node in Binary Search Tree def insert_node(root x): current = root parent = None # Traverse to the correct position for insertion while current is not None: parent = current if x < current.data: current = current.left else: current = current.right # Insert new Node at the correct position if parent is None: root = Node(x) elif x < parent.data: parent.left = Node(x) else: parent.right = Node(x) # DFS to populate parent map for each node def dfs(root parent_map parent=None): if root is None: return # Store the parent of the current node if parent is not None: parent_map[root] = parent # Recur for left and right children dfs(root.left parent_map root) dfs(root.right parent_map root) # Function to find the node with the given # value in the BST def find_node(root val): if root is None: return None if root.data == val: return root left_result = find_node(root.left val) if left_result: return left_result return find_node(root.right val) # Find maximum element in the path between # two nodes in BST def find_max_element(root x y): parent_map = {} # Populate parent map with DFS dfs(root parent_map) # Find the nodes corresponding to the # values x and y p1 = find_node(root x) p2 = find_node(root y) # If nodes not found if not p1 or not p2: return -1 # Sets to store nodes encountered # while traversing up the tree s1 = set() s2 = set() # Variable to store the maximum element in the path max_element = float('-inf') # Traverse up the tree from p1 and p2 # and add nodes to sets s1 and s2 while p1 != p2: if p1: s1.add(p1) max_element = max(max_element p1.data) # Move to parent node p1 = parent_map.get(p1) if p2: s2.add(p2) max_element = max(max_element p2.data) p2 = parent_map.get(p2) # Check if there's a common node in both sets if p2 in s1: break if p1 in s2: break # Now both p1 and p2 point to their # Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA) max_element = max(max_element p1.data) return max_element if __name__ == '__main__': arr = [18 36 9 6 12 10 1 8] a b = 1 10 n = len(arr) root = Node(arr[0]) for i in range(1 n): insert_node(root arr[i]) print(find_max_element(root a b))
// C# program to find the maximum element in the path // between two Nodes of Binary Search Tree. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Insert a new Node in Binary Search Tree static public void insertNode(Node root int x) { Node current = root parent = null; // Traverse to the correct position // for insertion while (current != null) { parent = current; if (x < current.data) current = current.left; else current = current.right; } // Insert new Node at the correct // position if (parent == null) root = new Node(x); else if (x < parent.data) parent.left = new Node(x); else parent.right = new Node(x); } // DFS to populate parent map for each node static public void dfs(Node root Dictionary<Node Node> parentMap Node parent) { if (root == null) return; // Store the parent of the current node if (parent != null) { parentMap[root] = parent; } // Recur for left and right children dfs(root.left parentMap root); dfs(root.right parentMap root); } // Function to find the node with the given // value in the BST static public Node findNode(Node root int val) { if (root == null) return null; if (root.data == val) return root; Node leftResult = findNode(root.left val); if (leftResult != null) return leftResult; return findNode(root.right val); } // Find maximum element in the path between // two nodes in BST static public int findMaxElement(Node root int x int y) { Dictionary<Node Node> parentMap = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); // Populate parent map with DFS dfs(root parentMap null); // Find the nodes corresponding to // the values x and y Node p1 = findNode(root x); Node p2 = findNode(root y); // If nodes not found if (p1 == null || p2 == null) return -1; // Sets to store nodes encountered // while traversing up the tree HashSet<Node> s1 = new HashSet<Node>(); HashSet<Node> s2 = new HashSet<Node>(); // Variable to store the maximum element // in the path int maxElement = int.MinValue; // Traverse up the tree from p1 and p2 // and add nodes to sets s1 and s2 while (p1 != p2) { if (p1 != null) { s1.Add(p1); maxElement = Math.Max(maxElement p1.data); // Move to parent node p1 = parentMap[p1]; } if (p2 != null) { s2.Add(p2); maxElement = Math.Max(maxElement p2.data); p2 = parentMap[p2]; } // Check if there's a common node in both sets if (s1.Contains(p2)) break; if (s2.Contains(p1)) break; } // Now both p1 and p2 point to their Lowest // Common Ancestor (LCA) maxElement = Math.Max(maxElement p1.data); return maxElement; } static void Main() { int[] arr = {18 36 9 6 12 10 1 8}; int a = 1 b = 10; int n = arr.Length; Node root = new Node(arr[0]); for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) insertNode(root arr[i]); Console.WriteLine(findMaxElement(root a b)); } }
// JavaScript program to find the maximum element in the path // between two Nodes of Binary Search Tree. class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = this.right = null; } } // Insert a new Node in Binary Search Tree function insertNode(root x) { let current = root parent = null; // Traverse to the correct position for insertion while (current !== null) { parent = current; if (x < current.data) current = current.left; else current = current.right; } // Insert new Node at the correct position if (parent === null) root = new Node(x); else if (x < parent.data) parent.left = new Node(x); else parent.right = new Node(x); } // DFS to populate parent map for each node function dfs(root parentMap parent = null) { if (root === null) return; // Store the parent of the current node if (parent !== null) { parentMap.set(root parent); } // Recur for left and right children dfs(root.left parentMap root); dfs(root.right parentMap root); } // Function to find the node with the given // value in the BST function findNode(root val) { if (root === null) return null; if (root.data === val) return root; let leftResult = findNode(root.left val); if (leftResult !== null) return leftResult; return findNode(root.right val); } // Find maximum element in the path // between two nodes in BST function findMaxElement(root x y) { let parentMap = new Map(); // Populate parent map with DFS dfs(root parentMap); // Find the nodes corresponding to the // values x and y let p1 = findNode(root x); let p2 = findNode(root y); // If nodes not found if (p1 === null || p2 === null) return -1; // Sets to store nodes encountered let s1 = new Set(); let s2 = new Set(); // Variable to store the maximum // element in the path let maxElement = -Infinity; // Traverse up the tree from p1 and p2 // and add nodes to sets s1 and s2 while (p1 !== p2) { if (p1 !== null) { s1.add(p1); maxElement = Math.max(maxElement p1.data); // Move to parent node p1 = parentMap.get(p1); } if (p2 !== null) { s2.add(p2); maxElement = Math.max(maxElement p2.data); p2 = parentMap.get(p2); } // Check if there's a common node in both sets if (s1.has(p2)) break; if (s2.has(p1)) break; } // Now both p1 and p2 point to their Lowest // Common Ancestor (LCA) maxElement = Math.max(maxElement p1.data); return maxElement; } let arr = [18 36 9 6 12 10 1 8]; let a = 1 b = 10; let n = arr.length; let root = new Node(arr[0]); for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) insertNode(root arr[i]); console.log(findMaxElement(root a b));
Ausgabe
12
[Erwarteter Ansatz] Verwendung der LCA von zwei Knoten – O(h)-Zeit und O(h)-Raum
Die Idee ist zu finden Niedrigster gemeinsamer Vorfahre von Knoten 'a' und Knoten 'b'. Suchen Sie dann nach dem maximalen Knoten zwischen LCA und „a“ und finden Sie auch den maximalen Knoten zwischen LCA und „b“. Die Antwort wird maximal zwei Knoten sein.
Unten ist die Implementierung des obigen Algorithmus:
C++// C++ program to find maximum element in the path // between two Nodes of Binary Search Tree. #include
// Java program to find maximum element in the path // between two Nodes of Binary Search Tree. import java.util.*; class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Insert a new Node in Binary Search Tree static void insertNode(Node root int x) { Node current = root parent = null; // Traverse to the correct // position for insertion while (current != null) { parent = current; if (x < current.data) current = current.left; else current = current.right; } // Insert new Node at the correct // position if (parent == null) root = new Node(x); else if (x < parent.data) parent.left = new Node(x); else parent.right = new Node(x); } // Find maximum element in the path from // an ancestor to a node static int maxInPath(Node root int x) { int maxElement = Integer.MIN_VALUE; Node current = root; // Traverse the path from root to the // target node 'x' while (current != null && current.data != x) { maxElement = Math.max(maxElement current.data); if (x < current.data) current = current.left; else current = current.right; } return Math.max(maxElement x); } // Find maximum element in the path between two // nodes in BST static int findMaxElement(Node root int x int y) { Node current = root; // Find Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA) of x and y while ((x < current.data && y < current.data) || (x > current.data && y > current.data)) { if (x < current.data && y < current.data) current = current.left; else if (x > current.data && y > current.data) current = current.right; } // Find maximum elements in paths from LCA // to x and LCA to y return Math.max(maxInPath(current x) maxInPath(current y)); } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {18 36 9 6 12 10 1 8}; int a = 1 b = 10; Node root = new Node(arr[0]); for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) insertNode(root arr[i]); System.out.println(findMaxElement(root a b)); } }
# Python program to find maximum element in the path # between two Nodes of Binary Search Tree. class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Insert a new Node in Binary Search Tree def insertNode(root x): current = root parent = None # Traverse to the correct position for insertion while current is not None: parent = current if x < current.data: current = current.left else: current = current.right # Insert new Node at the correct position if parent is None: root = Node(x) elif x < parent.data: parent.left = Node(x) else: parent.right = Node(x) # Find maximum element in the path from an # ancestor to a node def maxInPath(root x): maxElement = float('-inf') current = root # Traverse the path from root to the # target node 'x' while current is not None and current.data != x: maxElement = max(maxElement current.data) if x < current.data: current = current.left else: current = current.right return max(maxElement x) # Find maximum element in the path between # two nodes in BST def findMaxElement(root x y): current = root # Find Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA) of x and y while (x < current.data and y < current.data) or (x > current.data and y > current.data): if x < current.data and y < current.data: current = current.left elif x > current.data and y > current.data: current = current.right # Find maximum elements in paths from LCA to # x and LCA to y return max(maxInPath(current x) maxInPath(current y)) if __name__ == '__main__': arr = [18 36 9 6 12 10 1 8] a b = 1 10 root = Node(arr[0]) for i in range(1 len(arr)): insertNode(root arr[i]) print(findMaxElement(root a b))
// C# program to find maximum element in the path // between two Nodes of Binary Search Tree. using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Insert a new Node in Binary Search Tree static void insertNode(Node root int x) { Node current = root parent = null; // Traverse to the correct position // for insertion while (current != null) { parent = current; if (x < current.data) current = current.left; else current = current.right; } // Insert new Node at the correct position if (parent == null) root = new Node(x); else if (x < parent.data) parent.left = new Node(x); else parent.right = new Node(x); } // Find maximum element in the path from an // ancestor to a node static int maxInPath(Node root int x) { int maxElement = int.MinValue; Node current = root; // Traverse the path from root to the target node 'x' while (current != null && current.data != x) { maxElement = Math.Max(maxElement current.data); if (x < current.data) current = current.left; else current = current.right; } return Math.Max(maxElement x); } // Find maximum element in the path between two nodes in BST static int findMaxElement(Node root int x int y) { Node current = root; // Find Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA) of x and y while ((x < current.data && y < current.data) || (x > current.data && y > current.data)) { if (x < current.data && y < current.data) current = current.left; else if (x > current.data && y > current.data) current = current.right; } // Find maximum elements in paths from // LCA to x and LCA to y return Math.Max(maxInPath(current x) maxInPath(current y)); } static void Main() { int[] arr = {18 36 9 6 12 10 1 8}; int a = 1 b = 10; Node root = new Node(arr[0]); for (int i = 1; i < arr.Length; i++) insertNode(root arr[i]); Console.WriteLine(findMaxElement(root a b)); } }
// JavaScript program to find maximum element in the path // between two Nodes of Binary Search Tree. class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Insert a new Node in Binary Search Tree function insertNode(root x) { let current = root parent = null; // Traverse to the correct position for insertion while (current !== null) { parent = current; if (x < current.data) current = current.left; else current = current.right; } // Insert new Node at the correct position if (parent === null) root = new Node(x); else if (x < parent.data) parent.left = new Node(x); else parent.right = new Node(x); } // Find maximum element in the path from an // ancestor to a node function maxInPath(root x) { let maxElement = -Infinity; let current = root; // Traverse the path from root to the target node 'x' while (current !== null && current.data !== x) { maxElement = Math.max(maxElement current.data); if (x < current.data) current = current.left; else current = current.right; } return Math.max(maxElement x); } // Find maximum element in the path between // two nodes in BST function findMaxElement(root x y) { let current = root; // Find Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA) of x and y while ((x < current.data && y < current.data) || (x > current.data && y > current.data)) { if (x < current.data && y < current.data) current = current.left; else if (x > current.data && y > current.data) current = current.right; } // Find maximum elements in paths from LCA to // x and LCA to y return Math.max(maxInPath(current x) maxInPath(current y)); } const arr = [18 36 9 6 12 10 1 8]; const a = 1 b = 10; const root = new Node(arr[0]); for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { insertNode(root arr[i]); } console.log(findMaxElement(root a b));
Ausgabe
12Quiz erstellen

