Um Eingabe- und Ausgabevorgänge in C++ auszuführen, müssen wir iostream-Headerdateien verwenden. Ohne eine Header-Datei können wir keine Eingaben vom Benutzer entgegennehmen oder Ausgaben drucken.
Syntax der Header-Datei:
Java-Namenskonventionen
#include #include 'iostream.h'
Es gibt zwei Arten von Streams in der iostream-Headerdatei
1. Eingabestream : Um Eingaben vom Benutzer entgegenzunehmen, müssen wir cin verwenden, das zum Eingabestream gehört
Syntax zur Verwendung des Eingabestreams:
std::cin>>variable_name
Wenn cin ausgeführt wird, bleibt der Cursor bei der jeweiligen Anweisung stehen, bis der Wert eingegeben wird. Der eingegebene Wert wird in einer Variablen gespeichert.
2. Ausgabestream : Um die Ausgabe zu drucken, verwenden wir integrierte Funktionen im cout-Ausgabestream
Syntax für cout
std::cout<<variable_name < pre> <p>When cout is executed, the value in the variable will be printed.</p> <h3>Different operations in iostream</h3> <p> <strong>1. Cin</strong> </p> <p>Using cin, we can take input from the user and store the value in the variable. We need to use the cin keyword followed by >> and the variable name.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax:</strong> </p> <pre> std::cin>>variable_name </pre> <p>To use cin, we need to use <strong>#include </strong> as cin belongs to this header file, and without this, an error will occur.</p> <p> <strong>Example code for cin:</strong> </p> <pre> //using header file iostream #include using namespace std; int main() { string name; //cin declaration cin >> name; return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we used cin to take the input, so to use cin, we included header file. When the input is taken, the string input is stored in the name variable.</p> <p> <strong>2. Cout</strong> </p> <p>To print the output, we need to use the cout keyword, which belongs to the iostream header file. To use cout, we need to use the cout keyword followed by << and variable or the statement to print the output.</p> <p>The syntax for using cout:</p> <pre> std::cout<<variable_name < pre> <p> <strong>Example of using cout:</strong> </p> <pre> //to use the cout statement, we need to use the iostream header file #include using namespace std; int main() { //cout statement is used here to print the statement cout << 'Hi from cout statement'; return 0;} </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-2.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> :</p> <p>In the above code, we used a cout statement to print the statement. To use the cout statement, we need to include iostream.h header file. Once the cout is executed, statement or variable value will be printing the output. To print any statement, we need to use double quotes (' '), and to print a variable value; we need to use just the variable name without double quotes(' ')</p> <p> <strong>3. Cerr</strong> </p> <p>Cerr is used to print errors in C++, which is present in the iostream header file. If we need to print any error message in the code if any condition fails, then cerr is very helpful.</p> <p>The syntax for cerr is:</p> <pre> cerr<<variable_name < pre> <p>Example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<'the number entered in even number'<<endl; } else{ std::cerr << 'enter proper number' '
'; return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-3.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above example, we used cin to take the input and check if the given number is even or not. If the given number is not even, we need to print an error that the given number is not an even number. We use the cerr keyword in the iostream header file to print this error.</p> <p> <strong>4. Clog:</strong> </p> <p>The clog is also used to print error messages, but unlike cerr, clog is buffered, which means the error message is stored in a buffer and then will be printed, but cerr is unbuffered and will not store the error message in the buffer. The clog also belongs to the iostream header file. As the clog is buffered, it will not show the error message immediately. The clog is preferred more than cerr when efficiency is more important.</p> <p>The syntax for clog:</p> <pre> clog<<variable_name; < pre> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { clog << 'This message is stored in the buffer'; return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-4.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we are printing an error. To print this error, we use cerr, which belongs to the iostream header file. Before printing the error, we store the error in a buffer.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> : For all the input and output streams</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; string b; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<'the number entered is even enter a name'<>b; cout< <b; } else{ std::cerr << 'enter even number' '
'; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-5.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> : In the above code, we used all the input and output streams in the iostream.h header file.</p> <hr></b;></'the></pre></variable_name;></pre></'the></pre></variable_name></pre></variable_name></pre></variable_name> Um Cin zu verwenden, müssen wir verwenden #enthalten da cin zu dieser Header-Datei gehört und ohne diese ein Fehler auftritt.
Alphabet nach Zahlen
Beispielcode für cin:
//using header file iostream #include using namespace std; int main() { string name; //cin declaration cin >> name; return 0; } Ausgabe:
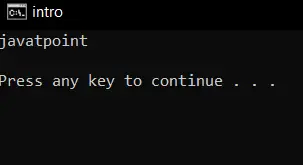
Erläuterung:
Im obigen Code haben wir cin für die Eingabe verwendet. Um cin zu verwenden, haben wir eine Header-Datei eingefügt. Wenn die Eingabe erfolgt, wird die Zeichenfolgeneingabe in der Namensvariablen gespeichert.
2. Cout
Um die Ausgabe zu drucken, müssen wir das Schlüsselwort cout verwenden, das zur iostream-Headerdatei gehört. Um cout zu verwenden, müssen wir das Schlüsselwort cout gefolgt von << und der Variablen oder der Anweisung zum Drucken der Ausgabe verwenden.
.net-Tutorial
Die Syntax für die Verwendung von cout:
std::cout<<variable_name < pre> <p> <strong>Example of using cout:</strong> </p> <pre> //to use the cout statement, we need to use the iostream header file #include using namespace std; int main() { //cout statement is used here to print the statement cout << 'Hi from cout statement'; return 0;} </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-2.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> :</p> <p>In the above code, we used a cout statement to print the statement. To use the cout statement, we need to include iostream.h header file. Once the cout is executed, statement or variable value will be printing the output. To print any statement, we need to use double quotes (' '), and to print a variable value; we need to use just the variable name without double quotes(' ')</p> <p> <strong>3. Cerr</strong> </p> <p>Cerr is used to print errors in C++, which is present in the iostream header file. If we need to print any error message in the code if any condition fails, then cerr is very helpful.</p> <p>The syntax for cerr is:</p> <pre> cerr<<variable_name < pre> <p>Example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\'the number entered in even number\'<<endl; } else{ std::cerr << \'enter proper number\' \'
\'; return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-3.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above example, we used cin to take the input and check if the given number is even or not. If the given number is not even, we need to print an error that the given number is not an even number. We use the cerr keyword in the iostream header file to print this error.</p> <p> <strong>4. Clog:</strong> </p> <p>The clog is also used to print error messages, but unlike cerr, clog is buffered, which means the error message is stored in a buffer and then will be printed, but cerr is unbuffered and will not store the error message in the buffer. The clog also belongs to the iostream header file. As the clog is buffered, it will not show the error message immediately. The clog is preferred more than cerr when efficiency is more important.</p> <p>The syntax for clog:</p> <pre> clog<<variable_name; < pre> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { clog << 'This message is stored in the buffer'; return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-4.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we are printing an error. To print this error, we use cerr, which belongs to the iostream header file. Before printing the error, we store the error in a buffer.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> : For all the input and output streams</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; string b; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\'the number entered is even enter a name\'<>b; cout< <b; } else{ std::cerr << \'enter even number\' \'
\'; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-5.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> : In the above code, we used all the input and output streams in the iostream.h header file.</p> <hr></b;></\'the></pre></variable_name;></pre></\'the></pre></variable_name></pre></variable_name> Ausgabe:

Erläuterung :
Im obigen Code haben wir eine cout-Anweisung verwendet, um die Anweisung zu drucken. Um die cout-Anweisung verwenden zu können, müssen wir die Header-Datei iostream.h einschließen. Sobald der Befehl ausgeführt wird, wird die Ausgabe durch die Anweisung oder den Variablenwert gedruckt. Um eine Anweisung zu drucken, müssen wir doppelte Anführungszeichen ('') verwenden und einen Variablenwert ausgeben; Wir müssen nur den Variablennamen ohne doppelte Anführungszeichen verwenden('')
3. Cerr
Pyspark
Cerr wird zum Drucken von Fehlern in C++ verwendet, die in der iostream-Headerdatei vorhanden sind. Wenn wir eine Fehlermeldung im Code ausgeben müssen, wenn eine Bedingung fehlschlägt, ist cerr sehr hilfreich.
Die Syntax für cerr lautet:
cerr<<variable_name < pre> <p>Example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\'the number entered in even number\'<<endl; } else{ std::cerr << \'enter proper number\' \'
\'; return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-3.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above example, we used cin to take the input and check if the given number is even or not. If the given number is not even, we need to print an error that the given number is not an even number. We use the cerr keyword in the iostream header file to print this error.</p> <p> <strong>4. Clog:</strong> </p> <p>The clog is also used to print error messages, but unlike cerr, clog is buffered, which means the error message is stored in a buffer and then will be printed, but cerr is unbuffered and will not store the error message in the buffer. The clog also belongs to the iostream header file. As the clog is buffered, it will not show the error message immediately. The clog is preferred more than cerr when efficiency is more important.</p> <p>The syntax for clog:</p> <pre> clog<<variable_name; < pre> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { clog << 'This message is stored in the buffer'; return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-4.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we are printing an error. To print this error, we use cerr, which belongs to the iostream header file. Before printing the error, we store the error in a buffer.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> : For all the input and output streams</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int main() { int a; string b; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\'the number entered is even enter a name\'<>b; cout< <b; } else{ std::cerr << \'enter even number\' \'
\'; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-5.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> : In the above code, we used all the input and output streams in the iostream.h header file.</p> <hr></b;></\'the></pre></variable_name;></pre></\'the></pre></variable_name> Ausgabe:

Erläuterung:
Im obigen Code geben wir einen Fehler aus. Um diesen Fehler auszudrucken, verwenden wir cerr, das zur iostream-Headerdatei gehört. Bevor wir den Fehler drucken, speichern wir den Fehler in einem Puffer.
Beispiel : Für alle Eingabe- und Ausgabestreams
#include using namespace std; int main() { int a; string b; cin>>a; if(a%2==0){ cout<<\\'the number entered is even enter a name\\'<>b; cout< <b; } else{ std::cerr << \\'enter even number\\' \\'
\\'; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/23/what-is-include-iostream-c-5.webp" alt="What is include iostream in C++"> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> : In the above code, we used all the input and output streams in the iostream.h header file.</p> <hr></b;></\\'the>