Der switch-Anweisung in C++ ist ein potenter Kontrollstruktur Dadurch können Sie mehrere Codesegmente basierend auf dem Ergebnis eines Ausdrucks ausführen. Es bietet einen raffinierten und effektiven Ersatz für die Verwendung einer Folge von if-else-if-Anweisungen wenn man sich zwischen mehreren Möglichkeiten entscheiden muss.
Die C++-Switch-Anweisung führt eine Anweisung unter mehreren Bedingungen aus. Es ist wie eine if-else-if-Leiteranweisung in C++.
switch(expression){ case value1: //code to be executed; break; case value2: //code to be executed; break; ...... default: //code to be executed if all cases are not matched; break; } 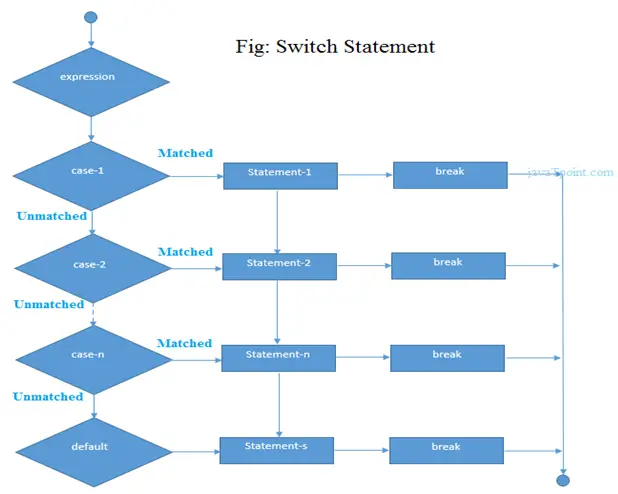
Beispiel für einen C++-Switch
#include using namespace std; int main () { int num; cout<>num; switch (num) { case 10: cout<<'it 20 is 10'; break; case 20: cout<<'it 20'; 30: 30'; default: cout<<'not 10, or } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a number: 10 It is 10 </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a number: 55 Not 10, 20 or 30 </pre> <h2>Features of Switch Statement:</h2> <p>There are several features of the <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> in C++. Some main features of the <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> in C are as follows:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>The <strong> <em>fall-through</em> </strong> behavior of the C++ <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> is one of its key features. The control will <strong> <em>fall through</em> </strong> to the next case if a <strong> <em>break statement</em> </strong> is not used to <strong> <em>stop</em> </strong> a case block. After that, subsequent cases will be processed until a <strong> <em>break</em> </strong> is encountered or the end of the <strong> <em>switch block</em> </strong> is reached. This capability may be purposely used to share common code across several scenarios.</li> <li>The <strong> <em>switch statement's</em> </strong> capacity to simplify code readability and maintenance is one of its fundamental advantages. Comparing a sequence of <strong> <em>nested if-else statements</em> </strong> to a <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> when dealing with many situations can provide clearer, more organized code. Each case label gives the program a unique and unambiguous path to follow, improving the codebase's overall readability. It is very advantageous when working with extensive and complicated programs, where maintaining a <strong> <em>logical flow</em> </strong> is crucial.</li> <li>Another noteworthy benefit of the switch statement is <strong> <em>efficiency</em> </strong> . When done correctly, a <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> may frequently be more effective than a succession of <strong> <em>if-else-if</em> </strong> This effectiveness results from the compiler's ability to optimize the switch statement to produce more effective machine code, which might lead to a quicker execution time. It's crucial to remember that the real speed improvements may differ based on the circumstance and compiler optimizations.</li> </ol> <h2>Limitations of Switch Statement</h2> <p>There are several limitations of the <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> in C++. Some main limitations of the <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> in C are as follows:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>The <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> has several restrictions, so it's important to be aware of those as well as industry standards. For instance, the <strong> <em>switch statement's</em> </strong> expression must be of the <strong> <em>integral</em> </strong> or <strong> <em>enumeration type</em> </strong> . It limits its ability to be used with other data types like <strong> <em>strings</em> </strong> or <strong> <em>floating-point integers</em> </strong> . Additionally, variables or expressions cannot be used as case labels since each case label must reflect a constant value that is known at <strong> <em>compile-time</em> </strong> .</li> <li>It is best practice to add a default case in the <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> to guarantee thorough case coverage. Instances where none of the preceding instances match the value of the phrase are handled by this case. When none of the predetermined situations apply, including a <strong> <em>default case</em> </strong> prevents unexpected behavior and offers a clear path of action.</li> </ol> <h2>Conclusion:</h2> <p>In conclusion, the <strong> <em>C++ switch statement</em> </strong> is a flexible construct that makes it easier for programs to handle a variety of scenarios. Its explicit <strong> <em>case labels</em> </strong> and succinct syntax make code easier to comprehend and maintain, especially in situations when there are many possible outcomes. The <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> improves the organization of program logic by offering a <strong> <em>direct mapping</em> </strong> between <strong> <em>cases</em> </strong> and <strong> <em>actions</em> </strong> . </p> <p>The <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> has advantages over an <strong> <em>if-else-if ladder</em> </strong> in terms of performance since the compiler can optimize it for <strong> <em>quicker execution</em> </strong> . Developers should be aware of its restrictions, such as the need for integral or enumeration expression types and constant case values.</p> <p>It is advised to provide a default case in the <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> to manage mismatched circumstances and use it efficiently and gently. Programmers may take advantage of the switch statement's advantages to create better <strong> <em>organized, effective</em> </strong> , and <strong> <em>understandable</em> </strong> C++ code by following best practices and comprehending its intricacies.</p> <hr></'it> Ausgabe:
Enter a number: 55 Not 10, 20 or 30
Merkmale der Switch-Anweisung:
Es gibt mehrere Funktionen des switch-Anweisung in C++. Einige Hauptmerkmale des switch-Anweisung in C sind wie folgt:
- Der durchfallen Verhalten von C++ switch-Anweisung ist eines seiner Hauptmerkmale. Die Kontrolle wird durchfallen zum nächsten Fall, wenn a break-Anweisung ist es nicht gewohnt stoppen ein Fallblock. Danach werden Folgefälle bis a. bearbeitet brechen angetroffen wird oder das Ende der Schalterblock ist erreicht. Diese Funktion kann gezielt genutzt werden, um gemeinsamen Code in mehreren Szenarios gemeinsam zu nutzen.
- Der switch-Anweisungen Die Fähigkeit, die Lesbarkeit und Wartung des Codes zu vereinfachen, ist einer seiner grundlegenden Vorteile. Vergleich einer Folge von verschachtelte if-else-Anweisungen zu einem switch-Anweisung Beim Umgang mit vielen Situationen kann ein klarerer und besser organisierter Code bereitgestellt werden. Jede Fallbezeichnung gibt dem Programm einen einzigartigen und eindeutigen Pfad, dem es folgen kann, und verbessert so die allgemeine Lesbarkeit der Codebasis. Es ist sehr vorteilhaft, wenn Sie mit umfangreichen und komplizierten Programmen arbeiten, bei denen die Wartung eines logischer Ablauf ist entscheidend.
- Ein weiterer bemerkenswerter Vorteil der switch-Anweisung ist Effizienz . Wenn es richtig gemacht wird, a switch-Anweisung kann häufig effektiver sein als eine Folge von wenn-sonst-wenn Diese Effektivität ergibt sich aus der Fähigkeit des Compilers, die Switch-Anweisung zu optimieren, um effektiveren Maschinencode zu erzeugen, was zu einer schnelleren Ausführungszeit führen kann. Es ist wichtig zu bedenken, dass die tatsächlichen Geschwindigkeitsverbesserungen je nach den Umständen und Compiler-Optimierungen unterschiedlich sein können.
Einschränkungen der Switch-Anweisung
Es gibt mehrere Einschränkungen switch-Anweisung in C++. Einige Haupteinschränkungen der switch-Anweisung in C sind wie folgt:
- Der switch-Anweisung Es gibt mehrere Einschränkungen, daher ist es wichtig, diese und die Industriestandards zu kennen. Zum Beispiel die switch-Anweisungen Der Ausdruck muss von der sein umfassend oder Aufzählungstyp . Es schränkt seine Fähigkeit ein, mit anderen Datentypen verwendet zu werden, z Saiten oder Gleitkomma-Ganzzahlen . Darüber hinaus können Variablen oder Ausdrücke nicht als Fallbeschriftungen verwendet werden, da jede Fallbeschriftung einen konstanten Wert widerspiegeln muss, der unter bekannt ist Kompilierzeit .
- Es empfiehlt sich, einen Standardfall hinzuzufügen switch-Anweisung um eine umfassende Fallabdeckung zu gewährleisten. Fälle, in denen keine der vorhergehenden Instanzen mit dem Wert der Phrase übereinstimmt, werden in diesem Fall behandelt. Wenn keine der vorgegebenen Situationen zutrifft, einschließlich a Standardfall verhindert unerwartetes Verhalten und bietet einen klaren Handlungspfad.
Abschluss:
Abschließend ist die C++-switch-Anweisung ist ein flexibles Konstrukt, das es Programmen erleichtert, mit einer Vielzahl von Szenarien umzugehen. Es ist explizit Kofferetiketten und eine prägnante Syntax erleichtern das Verständnis und die Pflege des Codes, insbesondere in Situationen, in denen es viele mögliche Ergebnisse gibt. Der switch-Anweisung Verbessert die Organisation der Programmlogik durch die Bereitstellung von a direkte Zuordnung zwischen Fälle Und Aktionen .
Der switch-Anweisung hat Vorteile gegenüber einem Wenn-sonst-wenn-Leiter in Bezug auf die Leistung, da der Compiler es optimieren kann schnellere Ausführung . Entwickler sollten sich der Einschränkungen bewusst sein, z. B. der Notwendigkeit von Integral- oder Aufzählungsausdruckstypen und konstanten Groß-/Kleinschreibungswerten.
Es wird empfohlen, einen Standardfall im anzugeben switch-Anweisung unpassende Umstände zu bewältigen und sie effizient und sanft zu nutzen. Programmierer können die Vorteile der Switch-Anweisung nutzen, um bessere Ergebnisse zu erzielen organisiert, effektiv , Und verständlich C++-Code, indem Sie Best Practices befolgen und seine Feinheiten verstehen.
