 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
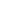
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }Gegeben a Binärer Baum Wandeln Sie es in ein um Zirkuläre doppelt verknüpfte Liste (In-Place).
- Die linken und rechten Zeiger in Knoten sollen als vorherige bzw. nächste Zeiger in der konvertierten kreisförmig verknüpften Liste verwendet werden.
- Die Reihenfolge der Knoten in der Liste muss mit der in Inorder für den angegebenen Binärbaum übereinstimmen.
- Der erste Knoten der Inorder-Traversierung muss der Kopfknoten der kreisförmigen Liste sein.
Beispiele:
Empfohlene Praxis Binärbaum zu CDLL Probieren Sie es aus!
Konvertieren Sie einen Binärbaum mithilfe der Rekursion in eine kreisförmige Liste mit doppelten Verknüpfungen:
Die Idee besteht darin, eine Allzweckfunktion zu erstellen, die zwei gegebene zirkuläre Doppellisten verkettet
Führen Sie die folgenden Schritte aus, um das Problem zu lösen:
- Konvertieren Sie den linken Teilbaum rekursiv in eine zirkuläre DLL. Sei die konvertierte Liste leftList .
- Konvertieren Sie den rechten Teilbaum rekursiv in eine zirkuläre DLL. Sei die konvertierte Liste rightList .
- Erstellen Sie eine kreisförmig verknüpfte Liste der Wurzeln des Baums und legen Sie fest, dass die linken und rechten Wurzelpunkte auf sich selbst zeigen.
- Verketten leftList mit der Liste des einzelnen Wurzelknotens.
- Verketten Sie die im obigen Schritt erstellte Liste mit rightList .
Notiz: Der obige Ansatz durchläuft den Baum im Postorder-Stil. Wir können auch in der Reihenfolge durchqueren. Wir können zuerst den linken Teilbaum und die Wurzel verketten, dann für den rechten Teilbaum wiederholen und das Ergebnis mit der Verkettung der linken Wurzel verketten.
Wie verketten Sie zwei zirkuläre DLLs?
- Holen Sie sich den letzten Knoten der linken Liste. Das Abrufen des letzten Knotens ist eine O(1)-Operation, da der vorherige Zeiger des Kopfes auf den letzten Knoten der Liste zeigt.
- Verbinden Sie es mit dem ersten Knoten der rechten Liste
- Holen Sie sich den letzten Knoten der zweiten Liste
- Verbinden Sie es mit dem Kopf der Liste.
Nachfolgend finden Sie Implementierungen der oben genannten Idee:
C++// C++ Program to convert a Binary Tree // to a Circular Doubly Linked List #include
// C Program to convert a Binary Tree // to a Circular Doubly Linked List #include
// Java Program to convert a Binary Tree to a // Circular Doubly Linked List // Node class represents a Node of a Tree class Node { int val; Node left right; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; left = right = null; } } // A class to represent a tree class Tree { Node root; public Tree() { root = null; } // concatenate both the lists and returns the head // of the List public Node concatenate(Node leftList Node rightList) { // If either of the list is empty then // return the other list if (leftList == null) return rightList; if (rightList == null) return leftList; // Store the last Node of left List Node leftLast = leftList.left; // Store the last Node of right List Node rightLast = rightList.left; // Connect the last node of Left List // with the first Node of the right List leftLast.right = rightList; rightList.left = leftLast; // left of first node refers to // the last node in the list leftList.left = rightLast; // Right of last node refers to the first // node of the List rightLast.right = leftList; // Return the Head of the List return leftList; } // Method converts a tree to a circular // Link List and then returns the head // of the Link List public Node bTreeToCList(Node root) { if (root == null) return null; // Recursively convert left and right subtrees Node left = bTreeToCList(root.left); Node right = bTreeToCList(root.right); // Make a circular linked list of single node // (or root). To do so make the right and // left pointers of this node point to itself root.left = root.right = root; // Step 1 (concatenate the left list with the list // with single node i.e. current node) // Step 2 (concatenate the returned list with the // right List) return concatenate(concatenate(left root) right); } // Display Circular Link List public void display(Node head) { System.out.println('Circular Linked List is :'); Node itr = head; do { System.out.print(itr.val + ' '); itr = itr.right; } while (itr != head); System.out.println(); } } // Driver Code class Main { public static void main(String args[]) { // Build the tree Tree tree = new Tree(); tree.root = new Node(10); tree.root.left = new Node(12); tree.root.right = new Node(15); tree.root.left.left = new Node(25); tree.root.left.right = new Node(30); tree.root.right.left = new Node(36); // head refers to the head of the Link List Node head = tree.bTreeToCList(tree.root); // Display the Circular LinkedList tree.display(head); } }
# Python3 Program to convert a Binary # Tree to a Circular Doubly Linked List class newNode: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.left = self.right = None # A function that appends rightList # at the end of leftList. def concatenate(leftList rightList): # If either of the list is empty # then return the other list if (leftList == None): return rightList if (rightList == None): return leftList # Store the last Node of left List leftLast = leftList.left # Store the last Node of right List rightLast = rightList.left # Connect the last node of Left List # with the first Node of the right List leftLast.right = rightList rightList.left = leftLast # Left of first node points to # the last node in the list leftList.left = rightLast # Right of last node refers to # the first node of the List rightLast.right = leftList return leftList # Function converts a tree to a circular # Linked List and then returns the head # of the Linked List def bTreeToCList(root): if (root == None): return None # Recursively convert left and # right subtrees left = bTreeToCList(root.left) right = bTreeToCList(root.right) # Make a circular linked list of single # node (or root). To do so make the # right and left pointers of this node # point to itself root.left = root.right = root # Step 1 (concatenate the left list # with the list with single # node i.e. current node) # Step 2 (concatenate the returned list # with the right List) return concatenate(concatenate(left root) right) # Display Circular Link List def displayCList(head): print('Circular Linked List is :') itr = head first = 1 while (head != itr or first): print(itr.data end=' ') itr = itr.right first = 0 print() # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': root = newNode(10) root.left = newNode(12) root.right = newNode(15) root.left.left = newNode(25) root.left.right = newNode(30) root.right.left = newNode(36) head = bTreeToCList(root) displayCList(head) # This code is contributed by PranchalK
// C# Program to convert a Binary Tree // to a Circular Doubly Linked List using System; // Node class represents a Node of a Tree public class Node { public int val; public Node left right; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; left = right = null; } } // A class to represent a tree public class Tree { internal Node root; public Tree() { root = null; } // concatenate both the lists // and returns the head of the List public virtual Node concatenate(Node leftList Node rightList) { // If either of the list is empty // then return the other list if (leftList == null) { return rightList; } if (rightList == null) { return leftList; } // Store the last Node of left List Node leftLast = leftList.left; // Store the last Node of right List Node rightLast = rightList.left; // Connect the last node of Left List // with the first Node of the right List leftLast.right = rightList; rightList.left = leftLast; // left of first node refers to // the last node in the list leftList.left = rightLast; // Right of last node refers to // the first node of the List rightLast.right = leftList; // Return the Head of the List return leftList; } // Method converts a tree to a circular // Link List and then returns the head // of the Link List public virtual Node bTreeToCList(Node root) { if (root == null) { return null; } // Recursively convert left // and right subtrees Node left = bTreeToCList(root.left); Node right = bTreeToCList(root.right); // Make a circular linked list of single // node (or root). To do so make the // right and left pointers of this node // point to itself root.left = root.right = root; // Step 1 (concatenate the left list with // the list with single node // i.e. current node) // Step 2 (concatenate the returned list // with the right List) return concatenate(concatenate(left root) right); } // Display Circular Link List public virtual void display(Node head) { Console.WriteLine('Circular Linked List is :'); Node itr = head; do { Console.Write(itr.val + ' '); itr = itr.right; } while (itr != head); Console.WriteLine(); } } // Driver Code public class GFG { public static void Main(string[] args) { // Build the tree Tree tree = new Tree(); tree.root = new Node(10); tree.root.left = new Node(12); tree.root.right = new Node(15); tree.root.left.left = new Node(25); tree.root.left.right = new Node(30); tree.root.right.left = new Node(36); // head refers to the head of the Link List Node head = tree.bTreeToCList(tree.root); // Display the Circular LinkedList tree.display(head); } } // This code is contributed by Shrikant13
<script> // javascript Program to convert a Binary Tree to a // Circular Doubly Linked List // Node class represents a Node of a Tree class Node { constructor(val) { this.val = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // A class to represent a var root = null; // concatenate both the lists and returns the head // of the List function concatenate(leftList rightList) { // If either of the list is empty then // return the other list if (leftList == null) return rightList; if (rightList == null) return leftList; // Store the last Node of left List var leftLast = leftList.left; // Store the last Node of right List var rightLast = rightList.left; // Connect the last node of Left List // with the first Node of the right List leftLast.right = rightList; rightList.left = leftLast; // left of first node refers to // the last node in the list leftList.left = rightLast; // Right of last node refers to the first // node of the List rightLast.right = leftList; // Return the Head of the List return leftList; } // Method converts a to a circular // Link List and then returns the head // of the Link List function bTreeToCList(root) { if (root == null) return null; // Recursively convert left and right subtrees var left = bTreeToCList(root.left); var right = bTreeToCList(root.right); // Make a circular linked list of single node // (or root). To do so make the right and // left pointers of this node point to itself root.left = root.right = root; // Step 1 (concatenate the left list with the list // with single node i.e. current node) // Step 2 (concatenate the returned list with the // right List) return concatenate(concatenate(left root) right); } // Display Circular Link List function display(head) { document.write('Circular Linked List is :
'); var itr = head; do { document.write(itr.val + ' '); itr = itr.right; } while (itr != head); document.write(); } // Driver Code // Build the root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(15); root.left.left = new Node(25); root.left.right = new Node(30); root.right.left = new Node(36); // head refers to the head of the Link List var head = bTreeToCList(root); // Display the Circular LinkedList display(head); // This code contributed by umadevi9616 </script>
Ausgabe
Circular Linked List is : 25 12 30 10 36 15
Zeitkomplexität: AN) Da jeder Knoten höchstens einmal besucht wird.
Nebenraum: O(log N) Der zusätzliche Platz wird im Rekursionsaufrufstapel verwendet, der bis zu einer maximalen Größe von logN anwachsen kann, da es sich um einen Binärbaum handelt.
Konvertieren Sie einen Binärbaum durch Inorder Traversal in eine kreisförmige Doppelverknüpfungsliste:
Die Idee besteht darin, den Binärbaum in der richtigen Reihenfolge zu durchlaufen. Verfolgen Sie beim Durchlaufen der Reihenfolge den zuvor besuchten Knoten beispielsweise in einer Variablen vorh . Machen Sie für jeden besuchten Knoten den nächsten Knoten vorh und setzen Sie den vorherigen Knoten als vorh .
Führen Sie die folgenden Schritte aus, um das Problem zu lösen:
So ermitteln Sie die Monitorgröße
- Konvertieren Sie zunächst den Binärbaum in eine doppelt verknüpfte Liste. Weitere Informationen finden Sie in diesem Beitrag Konvertieren Sie einen bestimmten Binärbaum in eine doppelt verknüpfte Liste .
- Konvertieren Sie nun diese doppelt verknüpfte Liste in eine kreisförmige doppelt verknüpfte Liste, indem Sie den ersten und letzten Knoten verbinden.
Nachfolgend finden Sie die Umsetzung des oben genannten Ansatzes.
C++// A C++ program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to // CDLL #include
// A Java program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to // CDLL // A binary tree node has - data left pointer and right // pointer class Node { int data; Node left right; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { Node root; // head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly // linked list Node head; // Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is // static so that the same value is accessible in all // recursive calls static Node prev = null; // A simple utility recursive function to convert a // given Binary tree to Doubly Linked List root --> Root // of Binary Tree void BTree2DoublyLinkedList(Node root) { // Base case if (root == null) return; // Recursively convert left subtree BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root.left); // Now convert this node if (prev == null) head = root; else { root.left = prev; prev.right = root; } prev = root; // Finally convert right subtree BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root.right); } // A simple function to convert a given binary tree to // Circular doubly linked list // using a utility function void BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(Node root) { BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root); // make the changes to convert a DLL to CDLL prev.right = head; head.left = prev; } /* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */ void printList(Node node) { if (node == null) return; Node curr = node; do { System.out.print(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.right; } while (curr != node); } // Driver program to test above functions public static void main(String[] args) { // Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = new Node(10); tree.root.left = new Node(12); tree.root.right = new Node(15); tree.root.left.left = new Node(25); tree.root.left.right = new Node(30); tree.root.right.left = new Node(36); // convert to DLL tree.BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(tree.root); // Print the converted List tree.printList(tree.head); } } // This code has been contributed by Abhijeet // Kumar(abhijeet19403)
# A python program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to DLL # A binary tree node has data left pointers and right pointers class Node: def __init__(self val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None # head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly linked list head = None # Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is # so that the same value is accessible in all recursive # calls prev = None # A simple recursive function to convert a given Binary tree # to Doubly Linked List # root --> Root of Binary Tree def BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root): # Base case if (root == None): return # Recursively convert left subtree BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.left) # Now convert this node global prev head if (prev == None): head = root else: root.left = prev prev.right = root prev = root # Finally convert right subtree BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.right) # Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list def printList(node): while (node != None): print(node.data) node = node.right # Driver program to test above functions # Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram root = Node(10) root.left = Node(12) root.right = Node(15) root.left.left = Node(25) root.left.right = Node(30) root.right.left = Node(36) # convert to DLL BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root) # Print the converted List printList(head) # This code is contributed by adityamaharshi21.
// A C# program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to // CDLL using System; public class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; left = right = null; } } public class BinaryTree { Node root; // head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly // linked list Node head; // Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is // static so that the same value is accessible in all // recursive calls static Node prev = null; // A simple utility recursive function to convert a // given Binary tree to Doubly Linked List root --> Root // of Binary Tree void BTree2DoublyLinkedList(Node root) { // Base case if (root == null) return; // Recursively convert left subtree BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root.left); // Now convert this node if (prev == null) head = root; else { root.left = prev; prev.right = root; } prev = root; // Finally convert right subtree BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root.right); } // A simple function to convert a given binary tree to // Circular doubly linked list // using a utility function void BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(Node root) { BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root); // make the changes to convert a DLL to CDLL prev.right = head; head.left = prev; } /* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */ void printList(Node node) { if (node == null) return; Node curr = node; do { Console.Write(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.right; } while (curr != node); } static public void Main() { // Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = new Node(10); tree.root.left = new Node(12); tree.root.right = new Node(15); tree.root.left.left = new Node(25); tree.root.left.right = new Node(30); tree.root.right.left = new Node(36); // convert to DLL tree.BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(tree.root); // Print the converted List tree.printList(tree.head); } } // This code is contributed by lokesh(lokeshmvs21).
// A javascript program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to DLL // A binary tree node has data left pointers and right pointers class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } var root; // head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly linked list var head; // Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is // so that the same value is accessible in all recursive // calls var prev = null; // A simple recursive function to convert a given Binary tree // to Doubly Linked List // root --> Root of Binary Tree function BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root) { // Base case if (root == null) return; // Recursively convert left subtree BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.left); // Now convert this node if (prev == null) head = root; else { root.left = prev; prev.right = root; } prev = root; // Finally convert right subtree BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.right); } /* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */ function printList(node) { while (node != null) { console.log(node.data + ' '); node = node.right; } } // Driver program to test above functions // Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(15); root.left.left = new Node(25); root.left.right = new Node(30); root.right.left = new Node(36); // convert to DLL BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root); // Print the converted List printList(head); // This code is contributed by ishankhandelwals.
Ausgabe
25 12 30 10 36 15
Zeitkomplexität: O(N) Da jeder Knoten höchstens einmal besucht wird.
Nebenraum: O(log N) Der zusätzliche Platz wird im rekursiven Funktionsaufrufstapel verwendet, der bis zu einer maximalen Größe von logN anwachsen kann.
Dieser Ansatz wurde beigesteuert von Abhijeet Kumar
