Wie funktionieren Cookies?
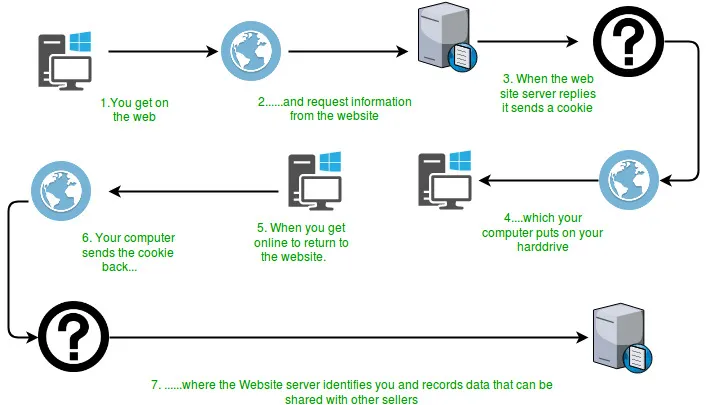 Wie aus dem obigen Diagramm ersichtlich ist, sendet der Server zusammen mit der Ressource ein Cookie-Objekt, das auf dem Computer des Clients gespeichert werden soll, wenn ein Benutzer zum ersten Mal eine Seite anfordert. Dieses Objekt könnte Details der Anfrage enthalten. Wenn der Benutzer später erneut dieselbe Ressource anfordert, sendet er zusammen mit der Anfrage das gespeicherte Cookie, das von Servern verwendet werden kann, um die Erfahrung des Benutzers weiter zu verbessern. Eigenschaften von Cookies:
Wie aus dem obigen Diagramm ersichtlich ist, sendet der Server zusammen mit der Ressource ein Cookie-Objekt, das auf dem Computer des Clients gespeichert werden soll, wenn ein Benutzer zum ersten Mal eine Seite anfordert. Dieses Objekt könnte Details der Anfrage enthalten. Wenn der Benutzer später erneut dieselbe Ressource anfordert, sendet er zusammen mit der Anfrage das gespeicherte Cookie, das von Servern verwendet werden kann, um die Erfahrung des Benutzers weiter zu verbessern. Eigenschaften von Cookies: - Zuerst setzt das Servlet ein Cookie mit dem Namen test_cookie. Andere Zeilen im Programm legen die Attribute des Cookies fest, z. B. den maximalen Domänenalterwert usw.
- Zweitens verwendet das Servlet request.getCookies, um alle eingehenden Cookies zu finden und ihre Namen und andere entsprechende Attribute anzuzeigen.
- Werden keine Cookies gefunden, wie es bei der ersten Anfrage der Fall ist, erscheint eine einfache Display-Meldung, die darauf hinweist, dass es sich um den ersten Besuch der Seite handelt.
Set-Cookie:session-id = 187-4969589-3049309
Set-Cookie: user = geek ;Domain =.foo.example.com
Set-Cookie: user = geek; Path =/ restricted
Set-Cookie: user = geek; expires = Wed 21-Feb-2017 15:23:00 IST
Set-Cookie: user = 'geek'; Max-Age = 3600Konstrukteur : Creates a cookie with specified name-value pair.
Syntax : public Cookie(String name String value) Parameters : name : name of the cookie value : value associated with this cookieMethoden:
Syntax : public void setDomain(String pattern) Parameters : pattern : string representing the domain in which this cookie is visible.
Syntax : public String getDomain()
Syntax : public void setComment(String purpose) Parameters : purpose : string representing the purpose of this cookie.
Syntax : public String getComment()
Syntax : public void setMaxAge(long time) Parameters : time : time in seconds before this cookie expires
Syntax : public String getMaxAge()
Syntax : public void setPath(String path) Parameters : path : path where this cookie is returned
Syntax : public String getMaxAge()
Syntax : public void setSecure(boolean secure) Parameters: secure - If true the cookie can only be sent over a secure protocol like https. If false it can be sent over any protocol.
Syntax : public boolean getSecure()
Syntax : public String getName()
Syntax : public void setValue(String newValue) Parameters : newValue - a String specifying the new value
Syntax : public String getValue()
Syntax : public int getVersion()
Syntax : public void setVersion(int v) Parameters : v - 0 for original Netscape specification; 1 for RFC 2965/2109
Syntax : public Cookie clone()Below is a Java implementation of a simple servlet program which stores a cookie in the browser when user first requests for it and then for further requests it displays the cookies stored. Java
// Java program to illustrate methods // of Cookie class import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.List; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.Cookie; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * Servlet implementation class cookieTest */ @WebServlet('/cookieTest') public class cookieTest extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /** * @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet() */ public cookieTest() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } /** * @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request HttpServletResponse * response) */ protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException IOException { response.setContentType('text/html'); // Create a new cookie with the name test cookie // and value 123 Cookie cookie = new Cookie('test_cookie' '123'); // setComment() method cookie.setComment('Just for testing'); // setDomain() method // cookie.setDomain('domain'); // setMaxAge() method cookie.setMaxAge(3600); // setPath() method cookie.setPath('/articles'); // setSecure() method cookie.setSecure(false); // setValue() method cookie.setValue('321'); // setVersion() method cookie.setVersion(0); response.addCookie(cookie); PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter(); pw.print(' '); Cookie ck[] = request.getCookies(); if (ck == null) { pw.print('This is first time the page is requested.
Stringformat
'); pw.print('And therefore no cookies found
'); } else { pw.print('Welcome Again...Cookies found
'); for (int i = 0; i < ck.length; i++) { // getName() method pw.print('Name :'
+ ck[i].getName() + ''); // getValue() method pw.print('Value :'
+ ck[i].getValue() + ''); // getDomain() method pw.print('Domain :'
+ ck[i].getDomain() + ''); // getPath() method pw.print('Name :'
+ ck[i].getPath() + ''); // getMaxAge() method pw.print('Max Age :'
+ ck[i].getMaxAge() + 'string int
'); // getComment() method pw.print('Comment :'
+ ck[i].getComment() + ''); // getSecure() method pw.print('Name :'
+ ck[i].getSecure() + ''); // getVersion() method pw.print('Version :'
+ ck[i].getVersion() + ''); } pw.print(' '); } pw.close(); } /** * @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request HttpServletResponse * response) */ protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException IOException { doGet(request response); } }
This is first time the page is requested. And therefore no cookies found.Zur zweiten Anfrage:
Welcome Again...Cookies found Name :test_cookie Value :321 Domain :null Name :null Max Age :-1 Comment :null Name :false Version :0
Wie führe ich das obige Programm aus?
Stellen Sie zunächst sicher, dass Sie einen Server wie Apache Tomcat installiert haben und mit dem von Ihnen verwendeten Tool wie Eclipse konfiguriert sind. Führen Sie einfach das obige Programm auf dem Server oder in Ihrem lokalen Browser aus, indem Sie die vollständige Adresse des von Ihnen verwendeten Serververzeichnisses eingeben. Das CookieTest-Servlet ist ein Servlet, das drei Aufgaben ausführt: