Die ROT13-Chiffre (gelesen als – um 13 Stellen drehen) ist ein Sonderfall der Ceaser-Chiffre, bei der die Verschiebung immer 13 beträgt.
Daher wird jeder Buchstabe um 13 Stellen verschoben, um die Nachricht zu verschlüsseln oder zu entschlüsseln.
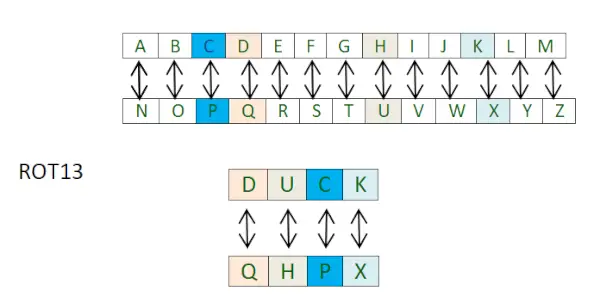
Sie müssen denken, dass es sich nur um eine weitere Caesar-Chiffre handelt Was ist dieses Mal anders? Nun, der Unterschied liegt in der Umsetzung. Der Ansatz besteht darin, zwei separate Python-Wörterbücher zu verwenden.
- Zuerst sucht man die verschiedenen Buchstaben nach ihrer Position im englischen Alphabet, um die verschobene Zahl zu erhalten
- Zweitens, um die Buchstaben zu erhalten, die diesen verschobenen Zahlen entsprechen.
Implementierung:
C++
// CPP program to implement> // ROT13 Caesar Cipher> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Map to lookup the index of alphabets> map <>char>,>int>>dict1;> // Map to lookup alphabets corresponding> // to the index after shift> map <>int>,>char>>dict2;> // Function to create map to lookup> void> create_dict()> {> >for>(>int> i = 1; i <27; i++)> >dict1[>char>(64 + i)] = i;> > >dict2[0] =>'Z'>;> > >for>(>int> i = 1; i <26; i++)> >dict2[i] =>char>(64 + i);> > >return>;> }> // Function to encrypt the string> // according to the shift provided> string encrypt(string message,>int> shift)> {> >string cipher =>''>;> >for>(>int> i = 0; i { // Checking for namespace if(message[i] != ' ') { // looks up the map and // adds the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]] + shift) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space cipher += ' '; } } return cipher; } // Function to decrypt the string // according to the shift provided string decrypt(string message, int shift) { string decipher = ''; for(int i = 0; i { // checks for space if(message[i] != ' ') { // looks up the map and // subtracts the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]] - shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space decipher += ' '; } } return decipher; } // Driver code int main() { create_dict(); string message = 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'; int shift = 13; cout << encrypt(message, shift) << '
'; message = 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'; shift = 13; cout << decrypt(message, shift) << '
'; return 0; } // This code is contributed by Sachin Bisht> |
Bash verkettet Zeichenfolgen
>
>
Java
// java program for the above approach> import> java.util.*;> public> class> Main {> >// Map to lookup the index of alphabets> >static> Map dict1 =>new> HashMap();> >// Map to lookup alphabets corresponding> >// to the index after shift> >static> Map dict2 =>new> HashMap();> >// Function to create map to lookup> >static> void> create_dict() {> >for>(>int> i =>1>; i <>27>; i++)> >dict1.put((>char>)(>64> + i), i);> >dict2.put(>0>,>'Z'>);> >for>(>int> i =>1>; i <>26>; i++)> >dict2.put(i, (>char>)(>64> + i));> >}> >// Function to encrypt the string> >// according to the shift provided> >static> String encrypt(String message,>int> shift) {> >String cipher =>''>;> >for>(>int> i =>0>; i // Checking for namespace if(message.charAt(i) != ' ') { // looks up the map and // adds the shift to the index int num = (dict1.get(message.charAt(i)) + shift) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2.get(num); } else { // adds space cipher += ' '; } } return cipher; } // Function to decrypt the string // according to the shift provided static String decrypt(String message, int shift) { String decipher = ''; for(int i = 0; i // checks for space if(message.charAt(i) != ' ') { // looks up the map and // subtracts the shift to the index int num = (dict1.get(message.charAt(i)) - shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2.get(num); } else { // adds space decipher += ' '; } } return decipher; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { create_dict(); String message = 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'; int shift = 13; System.out.println(encrypt(message, shift)); message = 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'; shift = 13; System.out.println(decrypt(message, shift)); } } // This code is contributed by prince> |
>
>
Python3
Was ist const in Java?
# Python program to implement> # ROT13 Caesar cipher> '''This script uses dictionaries instead of 'chr()' & 'ord()' function'''> # Dictionary to lookup the index of alphabets> dict1>=> {>'A'> :>1>,>'B'> :>2>,>'C'> :>3>,>'D'> :>4>,>'E'> :>5>,> >'F'> :>6>,>'G'> :>7>,>'H'> :>8>,>'I'> :>9>,>'J'> :>10>,> >'K'> :>11>,>'L'> :>12>,>'M'> :>13>,>'N'> :>14>,>'O'> :>15>,> >'P'> :>16>,>'Q'> :>17>,>'R'> :>18>,>'S'> :>19>,>'T'> :>20>,> >'U'> :>21>,>'V'> :>22>,>'W'> :>23>,>'X'> :>24>,>'Y'> :>25>,>'Z'> :>26>}> # Dictionary to lookup alphabets> # corresponding to the index after shift> dict2>=> {>0> :>'Z'>,>1> :>'A'>,>2> :>'B'>,>3> :>'C'>,>4> :>'D'>,>5> :>'E'>,> >6> :>'F'>,>7> :>'G'>,>8> :>'H'>,>9> :>'I'>,>10> :>'J'>,> >11> :>'K'>,>12> :>'L'>,>13> :>'M'>,>14> :>'N'>,>15> :>'O'>,> >16> :>'P'>,>17> :>'Q'>,>18> :>'R'>,>19> :>'S'>,>20> :>'T'>,> >21> :>'U'>,>22> :>'V'>,>23> :>'W'>,>24> :>'X'>,>25> :>'Y'>}> # Function to encrypt the string> # according to the shift provided> def> encrypt(message, shift):> >cipher>=> ''> >for> letter>in> message:> ># checking for space> >if>(letter !>=> ' '>):> ># looks up the dictionary and> ># adds the shift to the index> >num>=> ( dict1[letter]>+> shift )>%> 26> ># looks up the second dictionary for> ># the shifted alphabets and adds them> >cipher>+>=> dict2[num]> >else>:> ># adds space> >cipher>+>=> ' '> >return> cipher> # Function to decrypt the string> # according to the shift provided> def> decrypt(message, shift):> >decipher>=> ''> >for> letter>in> message:> ># checks for space> >if>(letter !>=> ' '>):> ># looks up the dictionary and> ># subtracts the shift to the index> >num>=> ( dict1[letter]>-> shift>+> 26>)>%> 26> ># looks up the second dictionary for the> ># shifted alphabets and adds them> >decipher>+>=> dict2[num]> >else>:> ># adds space> >decipher>+>=> ' '> >return> decipher> # driver function to run the program> def> main():> ># use 'upper()' function to convert any lowercase characters to uppercase> >message>=> 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'> >shift>=> 13> >result>=> encrypt(message.upper(), shift)> >print> (result)> >message>=> 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'> >shift>=> 13> >result>=> decrypt(message.upper(), shift)> >print> (result)> # Executes the main function> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> >main()> |
>
>
C#
Sammlungen in Java
using> System;> using> System.Collections;> using> System.Collections.Generic;> using> System.Linq;> // C# program for the above approach> class> HelloWorld {> > >// Map to lookup the index of alphabets> >public> static> Dictionary<>char>,>int>>dict1 =>new> Dictionary<>char>,>int>>();> >// Map to lookup alphabets corresponding> >// to the index after shift> >public> static> Dictionary<>int>,>char>>dict2 =>new> Dictionary<>int>,>char>>();> >// Function to create map to lookup> >public> static> void> create_dict() {> >for>(>int> i = 1; i <27; i++)> >dict1.Add((>char>)(64 + i), i);> >dict2.Add(0,>'Z'>);> >for>(>int> i = 1; i <26; i++)> >dict2.Add(i, (>char>)(64 + i));> >}> >// Function to encrypt the string> >// according to the shift provided> >public> static> string> encrypt(>string> message,>int> shift) {> >string> cipher =>''>;> >for>(>int> i = 0; i // Checking for namespace if(message[i] != ' ') { // looks up the map and // adds the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]] + shift) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space cipher += ' '; } } return cipher; } // Function to decrypt the string // according to the shift provided public static string decrypt(string message, int shift) { string decipher = ''; for(int i = 0; i // checks for space if(message[i] != ' ') { // looks up the map and // subtracts the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]]- shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space decipher += ' '; } } return decipher; } static void Main() { create_dict(); string message = 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'; int shift = 13; Console.WriteLine(encrypt(message, shift)); message = 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'; shift = 13; Console.WriteLine(decrypt(message, shift)); } } // The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.> |
>
>
Javascript
// Dictionary to lookup the index of alphabets> const dict1 = {>'A'>: 1,>'B'>: 2,>'C'>: 3,>'D'>: 4,>'E'>: 5,> >'F'>: 6,>'G'>: 7,>'H'>: 8,>'I'>: 9,>'J'>: 10,> >'K'>: 11,>'L'>: 12,>'M'>: 13,>'N'>: 14,>'O'>: 15,> >'P'>: 16,>'Q'>: 17,>'R'>: 18,>'S'>: 19,>'T'>: 20,> >'U'>: 21,>'V'>: 22,>'W'>: 23,>'X'>: 24,>'Y'>: 25,>'Z'>: 26};> // Dictionary to lookup alphabets> // corresponding to the index after shift> const dict2 = {0:>'Z'>, 1:>'A'>, 2:>'B'>, 3:>'C'>, 4:>'D'>, 5:>'E'>,> >6:>'F'>, 7:>'G'>, 8:>'H'>, 9:>'I'>, 10:>'J'>,> >11:>'K'>, 12:>'L'>, 13:>'M'>, 14:>'N'>, 15:>'O'>,> >16:>'P'>, 17:>'Q'>, 18:>'R'>, 19:>'S'>, 20:>'T'>,> >21:>'U'>, 22:>'V'>, 23:>'W'>, 24:>'X'>, 25:>'Y'>};> // Function to encrypt the string> // according to the shift provided> function> encrypt(message, shift) {> >let cipher =>''>;> >for> (let i = 0; i const letter = message[i]; // checking for space if (letter !== ' ') { // looks up the dictionary and // adds the shift to the index const num = (dict1[letter] + shift) % 26; // looks up the second dictionary for // the shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space cipher += ' '; } } return cipher; } // Function to decrypt the string // according to the shift provided function decrypt(message, shift) { let decipher = ''; for (let i = 0; i const letter = message[i]; // checks for space if (letter !== ' ') { // looks up the dictionary and // subtracts the shift to the index const num = (dict1[letter] - shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second dictionary for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space decipher += ' '; } } return decipher; } // driver function to run the program function main() { // use 'toUpperCase()' function to convert any lowercase characters to uppercase let message = 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'; let shift = 13; let result = encrypt(message.toUpperCase(), shift); console.log(result); message = 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'; shift = 13; result = decrypt(message.toUpperCase(), shift); console.log(result); } main(); // This code is contributed by adityashatmfh> |
>
>Ausgabe
TRRXF SBE TRRXF GEEKS FOR GEEKS>
Analyse: Die ROT13-Chiffre ist nicht sehr sicher, da sie nur ein Sonderfall der Caesar-Chiffre ist. Die Caesar-Chiffre kann entweder durch Frequenzanalyse oder durch einfaches Ausprobieren aller 25 Schlüssel gebrochen werden, während die ROT13-Chiffre durch einfaches Verschieben der Buchstaben um 13 Stellen gebrochen werden kann. Daher hat es keinen praktischen Nutzen.
Anwendung: ROT13 wurde Anfang der 1980er Jahre in der Newsgroup net.jokes verwendet.
