Ein Array ist die einfachste Datenstruktur in C, die homogene Daten an zusammenhängenden Speicherorten speichert. Wenn wir ein Array erstellen möchten, deklarieren wir den Datentyp und fügen ihm Elemente hinzu:
#include int main() { int i, arr[5] = {1, 2, 4, 2, 4}; for(i = 0; i <5; i++) { printf('%d ', arr[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 4 2 4 </pre> <p>In C, a Character and a String are separate data types, unlike other programming languages like Python. A String is a collection of Characters. Hence, to define a String, we use a Character Array:</p> <pre> #include int main() { char str[8]; printf('Enter a String: '); scanf('%s', &str); printf('%s', str); } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a String: Hello Hello </pre> <p>Now, we want to create an Array of Strings which means we are trying to create an Array of Character Arrays. We have two ways we can do this:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>Using Two-dimensional Arrays</li> <li>Using Pointers</li> </ol> <h3>Using Two-dimensional Arrays:</h3> <p>Creating a String Array is one of the applications of two-dimensional Arrays. To get a picture of the arrangement, observe the below representation:</p> <p>For suppose we want to create an Array of 3 Strings of size 5:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <p>Every String in a String Array must terminate with a null Character. It is the property of a String in C.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create a 2D Array:</strong> </p> <pre> Data_type name[rows][columns] = {{values in row 1}, {values in row 2}…}; </pre> <p> <strong>Syntax to create a String Array:</strong> </p> <pre> char Array[rows][columns] = {'String1', 'String2'...}; </pre> <p> <strong>Now, let us create an example String Array:</strong> </p> <ul> <li>Observe that when we assign the number of rows and columns, we need to consider the Null Character to the length.</li> </ul> <pre> #include int main() { int i; char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf('%s
', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Black Blame Block </pre> <ul> <li>char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Black'} -> {{'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'm', 'e', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}}</li> <li>We cannot directly manipulate the Strings in the Array as a String is an immutable data type. The compiler raises an error:</li> </ul> <pre> char Array[0] = 'Hello'; </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> [Error] assignment to expression with Array type </pre> <ul> <li>We can use the strcpy() function to copy the value by importing the String header file:</li> </ul> <pre> char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; strcpy(Array[0], 'Hello'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf('%s
', array[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Hello Blame Block </pre> <p> <strong>The Disadvantage of using 2D Arrays:</strong> </p> <p>Suppose we want to store 4 Strings in an Array: {'Java', 'T', 'point', 'JavaTpoint'}. We will store the Strings like this:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-2.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <ul> <li>The number of rows will be equal to the number of Strings, but the number of columns will equal the length of the longest String.</li> <li>The memory allocated to all the Strings will be the size of the longest String, causing ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> '.</li> <li>The orange part in the above representation is the memory wasted.</li> </ul> <h3>Using Pointers:</h3> <p>By using Pointers, we can avoid the Disadvantage of Memory wastage. But how do we do this?</p> <p>We need to create an Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Hence, we need to create an Array of type ' <strong>char*</strong> '. This way, all the Strings are stored elsewhere in the exactly needed memory, and the Pointers in the Array point to those memory locations causing no memory wastage. More specifically, the Pointers in the Array point to the first Character of the Strings.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Data Type* name[] = {'Value 1', 'Value 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of String Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>char* Array[] = {'String 1', 'String 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Representation:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-3.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <p> <strong>Now, let us create an example String Array:</strong> </p> <pre> #include #include int main() { int i; char* Array[] = {'HI', 'UP', 'AT'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf('%s
', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: HI UP AT </pre> <h3>Summary:</h3> <p>We cannot create a String Array like a normal one, as a String is an Array of Characters. We have two ways to do this:</p> <p> <strong>1. Using a Two-Dimensional Array:</strong> </p> <p>The Disadvantage of using this way is ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> ,' as the memory allocated to every String in the Array will be the memory required to store the longest String of the Array.</p> <p> <strong>2. Using Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Using Pointers, we create a single-dimensional Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Following this method can eliminate the 'Memory wastage' Disadvantage.</p> <hr></3;></pre></3;></pre></3;></pre></5;> In C sind ein Zeichen und ein String im Gegensatz zu anderen Programmiersprachen wie Python separate Datentypen. Ein String ist eine Sammlung von Zeichen. Um einen String zu definieren, verwenden wir daher ein Zeichenarray:
#include int main() { char str[8]; printf('Enter a String: '); scanf('%s', &str); printf('%s', str); } Ausgabe:
Enter a String: Hello Hello
Jetzt wollen wir ein Array aus Strings erstellen, was bedeutet, dass wir versuchen, ein Array aus Zeichen-Arrays zu erstellen. Wir haben zwei Möglichkeiten, dies zu tun:
- Verwendung zweidimensionaler Arrays
- Zeiger verwenden
Verwendung zweidimensionaler Arrays:
Das Erstellen eines String-Arrays ist eine der Anwendungen zweidimensionaler Arrays. Um sich ein Bild von der Anordnung zu machen, beachten Sie die folgende Darstellung:
Angenommen, wir möchten ein Array aus 3 Strings der Größe 5 erstellen:
dritte Normalform
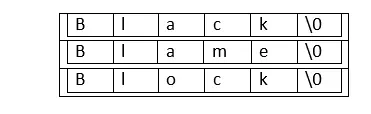
Jeder String in einem String-Array muss mit einem Nullzeichen enden. Es ist die Eigenschaft eines Strings in C.
Syntax zum Erstellen eines 2D-Arrays:
Data_type name[rows][columns] = {{values in row 1}, {values in row 2}…}; Syntax zum Erstellen eines String-Arrays:
Protokolle der Datenverbindungsschicht
char Array[rows][columns] = {'String1', 'String2'...}; Lassen Sie uns nun ein Beispiel-String-Array erstellen:
- Beachten Sie, dass wir bei der Zuweisung der Anzahl der Zeilen und Spalten das Nullzeichen für die Länge berücksichtigen müssen.
#include int main() { int i; char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Black Blame Block </pre> <ul> <li>char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Black'} -> {{'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'm', 'e', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}}</li> <li>We cannot directly manipulate the Strings in the Array as a String is an immutable data type. The compiler raises an error:</li> </ul> <pre> char Array[0] = 'Hello'; </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> [Error] assignment to expression with Array type </pre> <ul> <li>We can use the strcpy() function to copy the value by importing the String header file:</li> </ul> <pre> char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; strcpy(Array[0], 'Hello'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Hello Blame Block </pre> <p> <strong>The Disadvantage of using 2D Arrays:</strong> </p> <p>Suppose we want to store 4 Strings in an Array: {'Java', 'T', 'point', 'JavaTpoint'}. We will store the Strings like this:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-2.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <ul> <li>The number of rows will be equal to the number of Strings, but the number of columns will equal the length of the longest String.</li> <li>The memory allocated to all the Strings will be the size of the longest String, causing ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> '.</li> <li>The orange part in the above representation is the memory wasted.</li> </ul> <h3>Using Pointers:</h3> <p>By using Pointers, we can avoid the Disadvantage of Memory wastage. But how do we do this?</p> <p>We need to create an Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Hence, we need to create an Array of type ' <strong>char*</strong> '. This way, all the Strings are stored elsewhere in the exactly needed memory, and the Pointers in the Array point to those memory locations causing no memory wastage. More specifically, the Pointers in the Array point to the first Character of the Strings.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Data Type* name[] = {'Value 1', 'Value 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of String Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>char* Array[] = {'String 1', 'String 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Representation:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-3.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <p> <strong>Now, let us create an example String Array:</strong> </p> <pre> #include #include int main() { int i; char* Array[] = {'HI', 'UP', 'AT'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: HI UP AT </pre> <h3>Summary:</h3> <p>We cannot create a String Array like a normal one, as a String is an Array of Characters. We have two ways to do this:</p> <p> <strong>1. Using a Two-Dimensional Array:</strong> </p> <p>The Disadvantage of using this way is ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> ,' as the memory allocated to every String in the Array will be the memory required to store the longest String of the Array.</p> <p> <strong>2. Using Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Using Pointers, we create a single-dimensional Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Following this method can eliminate the 'Memory wastage' Disadvantage.</p> <hr></3;></pre></3;></pre></3;> - char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Black'} -> {{'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�' }, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'm', 'e', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}}
- Wir können die Strings im Array nicht direkt manipulieren, da ein String ein unveränderlicher Datentyp ist. Der Compiler gibt einen Fehler aus:
char Array[0] = 'Hello';
Ausgabe:
[Error] assignment to expression with Array type
- Wir können die Funktion strcpy() verwenden, um den Wert zu kopieren, indem wir die String-Header-Datei importieren:
char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; strcpy(Array[0], 'Hello'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Hello Blame Block </pre> <p> <strong>The Disadvantage of using 2D Arrays:</strong> </p> <p>Suppose we want to store 4 Strings in an Array: {'Java', 'T', 'point', 'JavaTpoint'}. We will store the Strings like this:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-2.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <ul> <li>The number of rows will be equal to the number of Strings, but the number of columns will equal the length of the longest String.</li> <li>The memory allocated to all the Strings will be the size of the longest String, causing ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> '.</li> <li>The orange part in the above representation is the memory wasted.</li> </ul> <h3>Using Pointers:</h3> <p>By using Pointers, we can avoid the Disadvantage of Memory wastage. But how do we do this?</p> <p>We need to create an Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Hence, we need to create an Array of type ' <strong>char*</strong> '. This way, all the Strings are stored elsewhere in the exactly needed memory, and the Pointers in the Array point to those memory locations causing no memory wastage. More specifically, the Pointers in the Array point to the first Character of the Strings.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Data Type* name[] = {'Value 1', 'Value 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of String Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>char* Array[] = {'String 1', 'String 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Representation:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-3.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <p> <strong>Now, let us create an example String Array:</strong> </p> <pre> #include #include int main() { int i; char* Array[] = {'HI', 'UP', 'AT'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: HI UP AT </pre> <h3>Summary:</h3> <p>We cannot create a String Array like a normal one, as a String is an Array of Characters. We have two ways to do this:</p> <p> <strong>1. Using a Two-Dimensional Array:</strong> </p> <p>The Disadvantage of using this way is ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> ,' as the memory allocated to every String in the Array will be the memory required to store the longest String of the Array.</p> <p> <strong>2. Using Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Using Pointers, we create a single-dimensional Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Following this method can eliminate the 'Memory wastage' Disadvantage.</p> <hr></3;></pre></3;> Der Nachteil der Verwendung von 2D-Arrays:
Angenommen, wir möchten 4 Strings in einem Array speichern: {'Java', 'T', 'point', 'JavaTpoint'}. Wir werden die Strings wie folgt speichern:

- Die Anzahl der Zeilen entspricht der Anzahl der Strings, aber die Anzahl der Spalten entspricht der Länge des längsten Strings.
- Der allen Strings zugewiesene Speicher hat die Größe des längsten Strings, was dazu führt, dass Speicherverschwendung '.
- Der orangefarbene Teil in der obigen Darstellung ist der verschwendete Speicher.
Verwendung von Zeigern:
Durch die Verwendung von Zeigern können wir den Nachteil der Speicherverschwendung vermeiden. Aber wie machen wir das?
Wir müssen ein Array von Zeigern erstellen, die auf Strings zeigen. Daher müssen wir ein Array vom Typ ' erstellen verkohlen* '. Auf diese Weise werden alle Strings an anderer Stelle im genau benötigten Speicher gespeichert und die Zeiger im Array verweisen auf diese Speicherorte, was keine Speicherverschwendung verursacht. Genauer gesagt zeigen die Zeiger im Array auf das erste Zeichen der Zeichenfolgen.
Syntax zum Erstellen eines Arrays von Zeigern:
Datentyp* name[] = {'Wert 1', 'Wert 2'…};
Syntax zum Erstellen eines Arrays von String-Zeigern:
Numpy-Summierung
char* Array[] = {'String 1', 'String 2'…};
Darstellung:

Lassen Sie uns nun ein Beispiel-String-Array erstellen:
#include #include int main() { int i; char* Array[] = {'HI', 'UP', 'AT'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: HI UP AT </pre> <h3>Summary:</h3> <p>We cannot create a String Array like a normal one, as a String is an Array of Characters. We have two ways to do this:</p> <p> <strong>1. Using a Two-Dimensional Array:</strong> </p> <p>The Disadvantage of using this way is ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> ,' as the memory allocated to every String in the Array will be the memory required to store the longest String of the Array.</p> <p> <strong>2. Using Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Using Pointers, we create a single-dimensional Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Following this method can eliminate the 'Memory wastage' Disadvantage.</p> <hr></3;> Zusammenfassung:
Wir können kein String-Array wie ein normales erstellen, da ein String ein Array von Zeichen ist. Wir haben zwei Möglichkeiten, dies zu tun:
1. Verwendung eines zweidimensionalen Arrays:
Der Nachteil dieser Methode ist: Speicherverschwendung ,‘, da der jedem String im Array zugewiesene Speicher der Speicher ist, der zum Speichern des längsten Strings des Arrays erforderlich ist.
2. Verwendung von Zeigern:
Mithilfe von Zeigern erstellen wir ein eindimensionales Array von Zeigern, die auf Strings zeigen. Mit dieser Methode kann der Nachteil der „Speicherverschwendung“ beseitigt werden.
