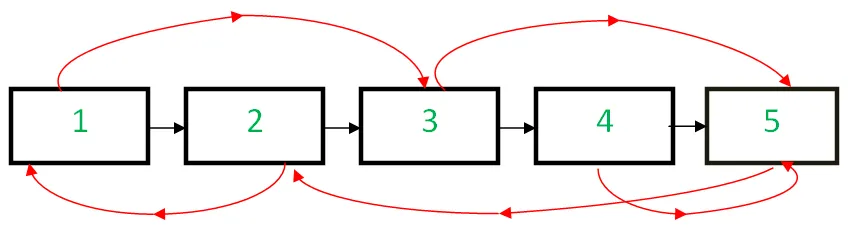
Gegeben a verlinkte Liste der Größe N wobei jeder Knoten zwei Links hat: nächster Zeiger zeigt auf den nächsten Knoten und zufälliger Zeiger zu einem beliebigen Knoten in der Liste. Die Aufgabe besteht darin, einen Klon dieser verknüpften Liste im O(1)-Bereich zu erstellen, d. h. ohne zusätzlichen Speicherplatz.
Beispiele:
Eingang: Kopf der unten verlinkten Liste
Ausgabe: Eine neue verknüpfte Liste, die mit der ursprünglichen Liste identisch ist.
[Erwarteter Ansatz] Durch direktes Einfügen von Knoten – O(3n)-Zeit und O(1)-Raum
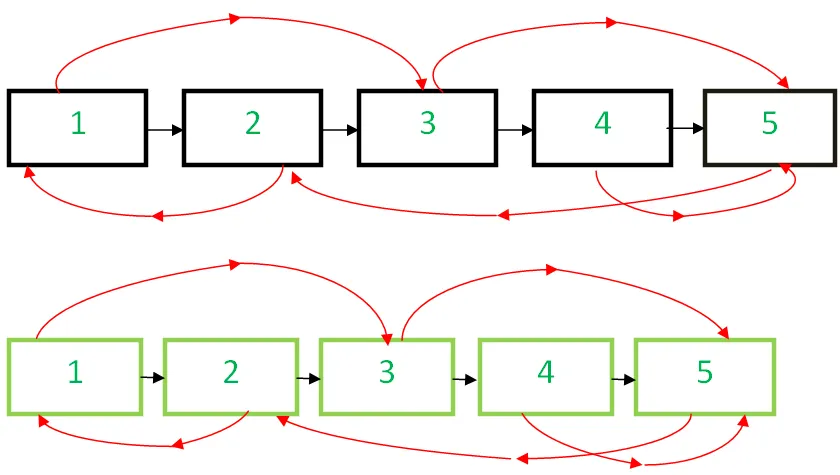
Die Idee besteht darin, ein Duplikat eines Knotens zu erstellen und es nicht in einer separaten Hash-Tabelle zu speichern, sondern zwischen dem ursprünglichen Knoten und dem nächsten Knoten einzufügen. Jetzt werden wir neue Knoten an alternativen Positionen haben. Nun zu einem Knoten X sein Duplikat wird sein X->nächster und der zufällige Zeiger des Duplikats sollte darauf zeigen X->zufällig->nächster (da das das Duplikat von ist X->zufällig ). Iterieren Sie also über die gesamte verknüpfte Liste, um den Zufallszeiger aller geklonten Knoten zu aktualisieren, und iterieren Sie dann erneut, um die ursprüngliche verknüpfte Liste und die geklonte verknüpfte Liste zu trennen.
Befolgen Sie die unten aufgeführten Schritte, um die Idee umzusetzen:
- Erstellen Sie die Kopie von Knoten 1 und dazwischen stecken Knoten 1 Und Knoten 2 Erstellen Sie in der ursprünglichen verknüpften Liste die Kopie von Knoten 2 und dazwischen stecken 2 nd Und 3 rd Knoten und so weiter. Fügen Sie die Kopie von N nach dem N hinzuThKnoten
- Verbinden Sie den Klonknoten, indem Sie die Zufallszeiger aktualisieren.
- Trennen Sie die geklonte verknüpfte Liste von der ursprünglichen Liste, indem Sie die nächsten Zeiger aktualisieren.
Nachfolgend finden Sie die Implementierung des oben genannten Ansatzes:
C++// C++ code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place #include
// Java code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node { int data; Node next random; Node(int x) { data = x; next = random = null; } } class GfG { // Function to clone the linked list static Node cloneLinkedList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } // Create new nodes and insert them next to the original nodes Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Node newNode = new Node(curr.data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr != null) { if (curr.random != null) { curr.next.random = curr.random.next; } curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; Node clonedHead = head.next; Node clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next != null) { // Update the next nodes of original node // and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original and cloned // linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list public static void printList(Node head) { while (head != null) { System.out.print(head.data + '('); if (head.random != null) { System.out.print(head.random.data); } else { System.out.print('null'); } System.out.print(')'); if (head.next != null) { System.out.print(' -> '); } head = head.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // Print the original list System.out.println('Original linked list:'); printList(head); // Function call Node clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); System.out.println('Cloned linked list:'); printList(clonedList); } }
# Python code to Clone a linked list with next and random # pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.random = None # Function to clone the linked list def clone_linked_list(head): if head is None: return None # Create new nodes and insert them next to # the original nodes curr = head while curr is not None: new_node = Node(curr.data) new_node.next = curr.next curr.next = new_node curr = new_node.next # Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head while curr is not None: if curr.random is not None: curr.next.random = curr.random.next curr = curr.next.next # Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head cloned_head = head.next clone = cloned_head while clone.next is not None: # Update the next nodes of original node # and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next clone.next = clone.next.next # Move pointers of original as well as # cloned linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next clone = clone.next curr.next = None clone.next = None return cloned_head # Function to print the linked list def print_list(head): while head is not None: print(f'{head.data}(' end='') if head.random: print(f'{head.random.data})' end='') else: print('null)' end='') if head.next is not None: print(' -> ' end='') head = head.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Creating a linked list with random pointer head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) head.random = head.next.next head.next.random = head head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next # Print the original list print('Original linked list:') print_list(head) # Function call cloned_list = clone_linked_list(head) print('Cloned linked list:') print_list(cloned_list)
// C# code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Node { public int Data; public Node next Random; public Node(int x) { Data = x; next = Random = null; } } class GfG { static Node CloneLinkedList(Node head) { if (head == null) return null; // Create new nodes and insert them next to // the original nodes Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Node newNode = new Node(curr.Data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr != null) { if (curr.Random != null) curr.next.Random = curr.Random.next; curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; Node clonedHead = head.next; Node clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next != null) { // Update the next nodes of original node // and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original as well as // cloned linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list static void PrintList(Node head) { while (head != null) { Console.Write(head.Data + '('); if (head.Random != null) Console.Write(head.Random.Data + ')'); else Console.Write('null)'); if (head.next != null) Console.Write(' -> '); head = head.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } public static void Main() { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.Random = head.next.next; head.next.Random = head; head.next.next.Random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.Random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.Random = head.next; // Print the original list Console.WriteLine('Original linked list:'); PrintList(head); Node clonedList = CloneLinkedList(head); Console.WriteLine('Cloned linked list:'); PrintList(clonedList); } }
// JavaScript code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } function cloneLinkedList(head) { if (head === null) { return null; } // Create new nodes and insert them next to the // original nodes let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { let newNode = new Node(curr.data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr !== null) { if (curr.random !== null) { curr.next.random = curr.random.next; } curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; let clonedHead = head.next; let clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next !== null) { // Update the next nodes of original node and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original as well as cloned // linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list function printList(head) { let result = ''; while (head !== null) { result += head.data + '('; result += head.random ? head.random.data : 'null'; result += ')'; if (head.next !== null) { result += ' -> '; } head = head.next; } console.log(result); } // Creating a linked list with random pointer let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // Print the original list console.log('Original linked list:'); printList(head); let clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); console.log('Cloned linked list:'); printList(clonedList);
Ausgabe
Original linked list: 1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2) Cloned linked list: 1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2)
Zeitkomplexität: O(3n) weil wir die verknüpfte Liste dreimal durchlaufen.
Hilfsraum: O(1) Da wir alle geklonten Knoten in der ursprünglichen verknüpften Liste selbst speichern, ist kein zusätzlicher Speicherplatz erforderlich.