1. Injektive (Eins-zu-Eins) Funktionen: Eine Funktion, bei der ein Element des Domänensatzes mit einem Element des Co-Domänensatzes verbunden ist.
2. Surjektive (Onto)-Funktionen: Eine Funktion, bei der jedes Element des Co-Domain-Sets ein Vorbild hat.
Beispiel: Betrachten Sie A = {1, 2, 3, 4}, B = {a, b, c} und f = {(1, b), (2, a), (3, c), (4, c) }.
Es handelt sich um eine surjektive Funktion, da jedes Element von B das Bild von A ist

Hinweis: In einer Onto-Funktion ist Range gleich Co-Domain.
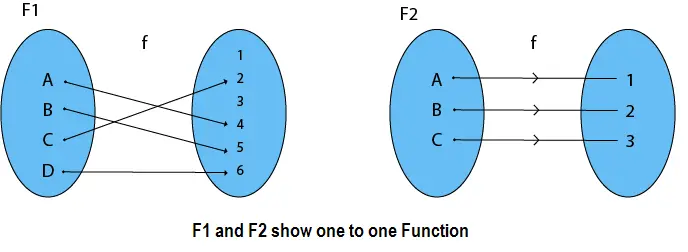
3. Bijektive (Eins-zu-Eins-Onto)-Funktionen: Eine Funktion, die sowohl injektiv (eins zu eins) als auch surjektiv (auf) ist, wird bijektive Funktion (eins zu eins auf) genannt.

Beispiel:
Consider P = {x, y, z} Q = {a, b, c} and f: P → Q such that f = {(x, a), (y, b), (z, c)} Das f ist eine Eins-zu-eins-Funktion und auch on. Es handelt sich also um eine bijektive Funktion.
4. In Funktionen: Eine Funktion, in der ein Element der Co-Domäne Y vorhanden sein muss, hat kein Vorbild in Domäne X.
Beispiel:
Wann endet Q1?
Consider, A = {a, b, c} B = {1, 2, 3, 4} and f: A → B such that f = {(a, 1), (b, 2), (c, 3)} In the function f, the range i.e., {1, 2, 3} ≠ co-domain of Y i.e., {1, 2, 3, 4} Daher handelt es sich um eine In-Funktion

5. Eins-Eins in Funktionen: Sei f: X → Y. Die Funktion f heißt Eins-Eins-In-Funktion, wenn verschiedene Elemente von
Beispiel:
Consider, X = {k, l, m} Y = {1, 2, 3, 4} and f: X → Y such that f = {(k, 1), (l, 3), (m, 4)} Die Funktion f ist eine Eins-Eins-In-Funktion

6. Many-One-Funktionen: Sei f: X → Y. Die Funktion f heißt Viele-Eins-Funktion, wenn in
Beispiel:
Consider X = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} Y = {x, y, z} and f: X → Y such that f = {(1, x), (2, x), (3, x), (4, y), (5, z)} Die Funktion f ist eine Viele-Eins-Funktion

7. Many-One in Funktionen: Sei f:
Beispiel:
Consider X = {a, b, c} Y = {1, 2} and f: X → Y such that f = {(a, 1), (b, 1), (c, 1)} Da die Funktion f eine Viele-Eins-Into-Funktion ist, ist sie auch eine Viele-Eins-Into-Funktion.

8. Many-One-Onto-Funktionen: Sei f:
Beispiel:
Consider X = {1, 2, 3, 4} Y = {k, l} and f: X → Y such that f = {(1, k), (2, k), (3, l), (4, l)} Die Funktion f ist eine Viele-Eins-Funktion (da die beiden Elemente das gleiche Bild in Y haben) und sie ist on (da jedes Element von Y das Bild eines Elements X ist). Es handelt sich also um eine Viele-Eins-Funktion

