Der asList() Methode von java.util.Arrays Die Klasse wird verwendet, um eine Liste fester Größe zurückzugeben, die durch das angegebene Array unterstützt wird. Diese Methode fungiert als Brücke zwischen Array-basierten und Sammlungs-basierten APIs , in Kombination mit Collection.toArray(). Die zurückgegebene Liste ist serialisierbar und implementiert RandomAccess.
Tipp: Dies läuft in O(1)-Zeit.
Syntax:
public static List asList(T... a)>
Parameter: Diese Methode übernimmt die Array a die in eine Liste umgewandelt werden muss. Hier … ist bekannt als vararg Dabei handelt es sich um ein Array von Parametern, das ähnlich wie ein Objekt-Array-Parameter funktioniert.
Spezielle Notiz: Bei primitiven Datentypen (int, float usw.) muss der Array-Typ eine Wrapper-Klasse (Integer, Float usw.) sein, d. h. Sie können int a[] nicht übergeben, aber Sie können Integer a[] übergeben. Wenn Sie int a[] übergeben, gibt diese Funktion eine List und keine List zurück, da in diesem Fall kein Autoboxing stattfindet und int a[] selbst als Objekt identifiziert wird und anstelle einer Liste eine Liste mit int-Arrays zurückgegeben wird von ganzen Zahlen, die in verschiedenen Sammlungsfunktionen zu Fehlern führen.
Rückgabewert: Diese Methode gibt a zurück Listenansicht des angegebenen Arrays.
Beispiel 1:
Java
Wer ist Urfi Javed?
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class for a string value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of String type> >String a[]> >=>new> String[] {>'A'>,>'B'>,>'C'>,>'D'> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements in list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statement> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Ausgabe
The list is: [A, B, C, D]>
Beispiel 2:
Java
Linux-Verzeichnis umbenennen
Java-PGM
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class For an integer value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements inside list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statements> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Ausgabe
The list is: [10, 20, 30, 40]>
Beispiel 3:
Java
Zeichenfolge zu lang
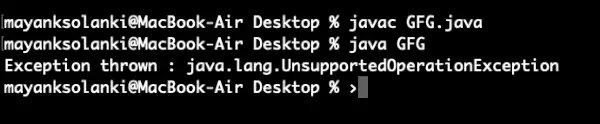
// Java Program to demonstrate asList() method> // Which returns fixed size list and> // throws UnsupportedOperationException> // if any element is added using add() method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Adding another int to the list> >// As Arrays.asList() returns fixed size> >// list, we'll get> >// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException> >list.add(>50>);> >// Printing all the elements of list> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (UnsupportedOperationException e) {> >// Display message when exception occurs> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>
Ausgabe: