Geben Sie eine ganze Zahl n an, die die Anzahl der Schnitte angibt, die an einem Pfannkuchen gemacht werden können, und ermitteln Sie die maximale Anzahl an Stücken, die durch n Schnitte gebildet werden können.
Beispiele:
Java virtuelle Maschine
Input : n = 1 Output : 2 With 1 cut we can divide the pancake in 2 pieces Input : 2 Output : 4 With 2 cuts we can divide the pancake in 4 pieces Input : 3 Output : 7 We can divide the pancake in 7 parts with 3 cuts Input : 50 Output : 1276
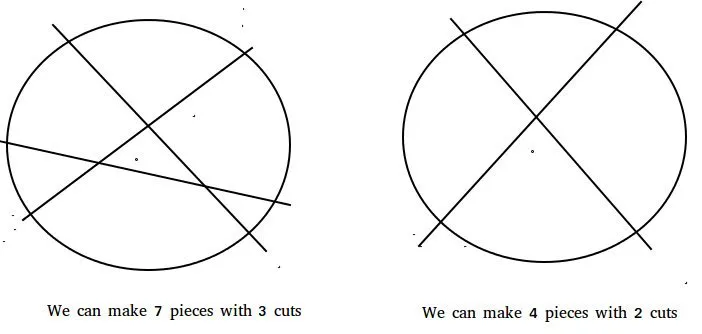
Let f(n) denote the maximum number of pieces that can be obtained by making n cuts. Trivially f(0) = 1 As there'd be only 1 piece without any cut. Similarly f(1) = 2 Proceeding in similar fashion we can deduce the recursive nature of the function. The function can be represented recursively as : f(n) = n + f(n-1) Hence a simple solution based on the above formula can run in O(n).
Wir können die obige Formel optimieren.
We now know f(n) = n + f(n-1) Expanding f(n-1) and so on we have f(n) = n + n-1 + n-2 + ...... + 1 + f(0) which gives f(n) = (n*(n+1))/2 + 1
Daher können wir mit dieser Optimierung alle Abfragen in O(1) beantworten.
Nachfolgend finden Sie die Umsetzung der obigen Idee:
// A C++ program to find the solution to // The Lazy Caterer's Problem #include
// Java program to find the solution to // The Lazy Caterer's Problem import java.io.*; class GFG { // This function returns the maximum // number of pieces that can be made // form pancake using n cuts static int findPieces(int n) { // Use the formula return (n * (n + 1)) / 2 + 1; } // Driver program to test above function public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println(findPieces(1)); System.out.println(findPieces(2)); System.out.println(findPieces(3)); System.out.println(findPieces(50)); } } // This code is contributed by Pramod Kumar
# A Python 3 program to # find the solution to # The Lazy Caterer's Problem # This function receives an # integer n and returns the # maximum number of pieces # that can be made form # pancake using n cuts def findPieces( n ): # Use the formula return (n * ( n + 1)) // 2 + 1 # Driver Code print(findPieces(1)) print(findPieces(2)) print(findPieces(3)) print(findPieces(50)) # This code is contributed # by ihritik
// C# program to find the solution // to The Lazy Caterer's Problem using System; class GFG { // This function returns the maximum // number of pieces that can be made // form pancake using n cuts static int findPieces(int n) { // Use the formula return (n * (n + 1)) / 2 + 1; } // Driver code public static void Main () { Console.WriteLine(findPieces(1)); Console.WriteLine(findPieces(2)); Console.WriteLine(findPieces(3)); Console.Write(findPieces(50)); } } // This code is contributed by Nitin Mittal.
// A php program to find // the solution to The // Lazy Caterer's Problem // This function receives // an integer n and returns // the maximum number of // pieces that can be made // form pancake using n cuts function findPieces($n) { // Use the formula return ($n * ( $n + 1)) / 2 + 1; } // Driver Code echo findPieces(1) 'n' ; echo findPieces(2) 'n' ; echo findPieces(3) 'n' ; echo findPieces(50) 'n'; // This code is contributed // by nitin mittal. ?> <script> // Javascript program to find the solution to // The Lazy Caterer's Problem // This function returns the maximum // number of pieces that can be made // form pancake using n cuts function findPieces(n) { // Use the formula return (n * (n + 1)) / 2 + 1; } // Driver Code document.write(findPieces(1) + '
'); document.write(findPieces(2) + '
'); document.write(findPieces(3) + '
'); document.write(findPieces(50)); </script>
Ausgabe :
2 4 7 1276
Referenzen: oeis.org
